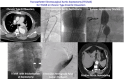
Transcatheter electrosurgical aortic septostomy optimizes distal landing zone in chronic dissection
- PMID: 39478927
- PMCID: PMC11518863
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xjtc.2024.07.007
Transcatheter electrosurgical aortic septostomy optimizes distal landing zone in chronic dissection
Abstract
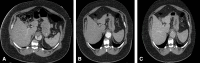
Objective: Efficacy of thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TEVAR) for chronic type B aortic dissection (CTBAD) is dependent on eliminating retrograde false lumen perfusion and remodeling the aorta. We describe the efficacy of a novel transcatheter electrosurgical technique to fenestrate the dissection flap and create a distal seal zone for TEVAR in CTBAD.
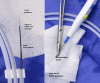
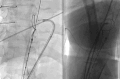
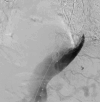
Methods: A retrospective review of the Emory Aortic Database from 2016 to 2023 identified 33 patients who underwent TEVAR with intentional endovascular rupture of the dissection flap (Knickerbocker; KNICK) for CTBAD. In 11 patients, we performed transcatheter electrosurgical aortic septostomy (TECSAS) before KNICK. The technical aspects of TECSAS + KNICK are described and results compared with TEVAR + KNICK alone.
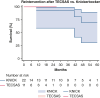
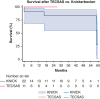
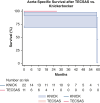
Results: Dissection chronicity, aortic size, and preoperative demographics were similar between groups. Technical success was 100%, with zero stroke or paraplegia in both groups. Thirty-day mortality for TECSAS versus KNICK was 0% versus 13.6% (P = .199). Median follow-up was shorter after TECSAS versus KNICK, although not statistically significant (14.6 months vs 21.9 months; P = .065). Elimination of retrograde false lumen perfusion (TECSAS 100% vs KNICK 68.2%; P = .035) and complete false lumen thrombosis or obliteration (TECSAS 91.9% vs KNICK 54.6%; P = .037) were more frequent after the TECSAS procedure. Aortic reinterventions were less frequent after TECSAS versus KNICK (0% vs 13.6%, P = .199), although not statistically significant.
Conclusions: The addition of TECSAS to intentional endovascular rupture of the dissection flap in CTBAD improves distal seal, eliminating retrograde false lumen perfusion. This technique is a safe and precise method to fenestrate a dissection flap and optimize TEVAR in CTBAD.
Keywords: aortic dissection; aortic septostomy; chronic type B aortic dissection (CTBAD); electrosurgical; thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TEVAR).
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Y.M.D. serves as a consultant for Cook Medical. W.D.J. serves as a consultant for Gore, Medtronic, Cook Medical, and Endologix. V.C.B. serves as a consultant for Edwards, Abbott, Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and Transmural Systems, Inc. B.G.L. serves as a consultant for Endospan and as a Speaker's Bureau for Medtronic. All other authors reported no conflicts of interest. The Journal policy requires editors and reviewers to disclose conflicts of interest and to decline handling or reviewing manuscripts for which they may have a conflict of interest. The editors and reviewers of this article have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Laser-assisted "Scissor" Technique to Facilitate Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair for Chronic Type B Aortic Dissection.Ann Vasc Surg. 2021 Nov;77:347.e7-347.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2021.04.048. Epub 2021 Jun 26. Ann Vasc Surg. 2021. PMID: 34182117
-
Impact of proximal seal zone length and intramural hematoma on clinical outcomes and aortic remodeling after thoracic endovascular aortic repair for aortic dissections.J Vasc Surg. 2019 Apr;69(4):987-995. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2018.06.219. Epub 2018 Oct 24. J Vasc Surg. 2019. PMID: 30528404
-
Modified Petticoat Technique with Pre-placement of a Distal Bare Stent Improves Early Aortic Remodeling after Complicated Acute Stanford Type B Aortic Dissection.Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2015 Oct;50(4):450-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2015.04.035. Epub 2015 Jun 19. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2015. PMID: 26100449
-
Intentional Targeted False Lumen Occlusion after Aortic Dissection: A Systematic Review of the Literature.Ann Vasc Surg. 2019 Apr;56:317-329. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2018.08.086. Epub 2018 Nov 26. Ann Vasc Surg. 2019. PMID: 30496905
-
Techniques and outcomes of false lumen embolization in chronic type B aortic dissection.J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2018 Dec;59(6):784-788. doi: 10.23736/S0021-9509.18.10638-0. Epub 2018 Jun 26. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2018. PMID: 29943961 Review.
References
-
- Kang W.C., Greenberg R.K., Mastracci T.M., et al. Endovascular repair of complicated chronic distal aortic dissections: intermediate outcomes and complications. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011;142(5):1074–1083. - PubMed
-
- Leshnower B.G., Szeto W.Y., Pochettino A., et al. Thoracic endografting reduces morbidity and remodels the thoracic aorta in DeBakey III aneurysms. Ann Thorac Surg. 2013;95(3):914–921. - PubMed
-
- Rohlffs F., Spanos K., Tsilimparis N., Debus E.S., Kolbel T. Techniques and outcomes of false lumen embolization in chronic type B aortic dissection. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 2018;59(6):784–788. - PubMed
-
- Kölbel T., Carpenter S.W., Lohrenz C., Tsilimparis N., Larena-Avellaneda A., Debus E.S. Addressing persistent false lumen flow in chronic aortic dissection: the knickerbocker technique. J Endovasc Ther. 2014;21(1):117–122. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

