Identification of middle cerebral artery stenosis in transcranial Doppler using a modified VGG-16
- PMID: 39479004
- PMCID: PMC11521853
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1394435
Identification of middle cerebral artery stenosis in transcranial Doppler using a modified VGG-16
Abstract
Objectives: The diagnosis of intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis (ICAS) is of great significance for the prevention of stroke. Deep learning (DL)-based artificial intelligence techniques may aid in the diagnosis. The study aimed to identify ICAS in the middle cerebral artery (MCA) based on a modified DL model.
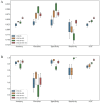
Methods: This retrospective study included two datasets. Dataset1 consisted of 3,068 transcranial Doppler (TCD) images of the MCA from 1,729 patients, which were assessed as normal or stenosis by three physicians with varying levels of experience, in conjunction with other medical imaging data. The data were used to improve and train the VGG16 models. Dataset2 consisted of TCD images of 90 people who underwent physical examination, which were used to verify the robustness of the model and compare the consistency between the model and human physicians.
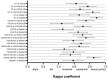
Results: The accuracy, precision, specificity, sensitivity, and area under curve (AUC) of the best model VGG16 + Squeeze-and-Excitation (SE) + skip connection (SC) on dataset1 reached 85.67 ± 0.43(%),87.23 ± 1.17(%),87.73 ± 1.47(%),83.60 ± 1.60(%), and 0.857 ± 0.004, while those of dataset2 were 93.70 ± 2.80(%),62.65 ± 11.27(%),93.00 ± 3.11(%),100.00 ± 0.00(%), and 0.965 ± 0.016. The kappa coefficient showed that it reached the recognition level of senior doctors.
Conclusion: The improved DL model has a good diagnostic effect for MCV stenosis in TCD images and is expected to help in ICAS screening.
Keywords: ICAS; deep learning; screening; stroke; transcranial Doppler.
Copyright © 2024 Xu, Li, Su, Qiu, Tong, Huang and Yao.
Conflict of interest statement
Dong Xu and Hao Li are co-inventors of a Chinese patent application (not yet granted) that includes some of the material used in this manuscript. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, Adeoye OM, Bambakidis NC, Becker K, et al. . 2018 guidelines for the early Management of Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. (2018) 49:e46–e110. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000158, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mattioni A, Cenciarelli S, Eusebi P, Brazzelli M, Mazzoli T, del Sette M, et al. . Transcranial Doppler sonography for detecting stenosis or occlusion of intracranial arteries in people with acute ischaemic stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2020) 2:CD010722. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010722.pub2, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

