NK Cells: Not Just Followers But Also Initiators of Chronic Vascular Rejection
- PMID: 39479216
- PMCID: PMC11521863
- DOI: 10.3389/ti.2024.13318
NK Cells: Not Just Followers But Also Initiators of Chronic Vascular Rejection
Abstract
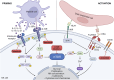
Chronic graft rejection represents a significant threat to long-term graft survival. Early diagnosis, understanding of the immunological mechanisms and appropriate therapeutic management are essential to improve graft survival and quality of life for transplant patients. Knowing which immune cells are responsible for chronic vascular rejection would allow us to provide effective and appropriate treatment for these patients. It is now widely accepted that natural killer (NK) cells play an important role in chronic vascular rejection. They can either initiate chronic vascular rejection by recognizing missing self on the graft or be recruited by donor-specific antibodies to destroy the graft during antibody-mediated rejection. Whatever the mechanisms of activation of NK cells, they need to be primed to become fully activated and damaging to the graft. A better understanding of the signaling pathways involved in NK cell priming and activation would pave the way for the development of new therapeutic strategies to cure chronic vascular rejection. This review examines the critical role of NK cells in the complex context of chronic vascular rejection.
Keywords: antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity; antibody mediated rejection; chronic rejection; missing self; natural killer cells.
Copyright © 2024 Chambon and Koenig.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of newer immunosuppressive regimens in renal transplantation: a systematic review and modelling study.Health Technol Assess. 2005 May;9(21):1-179, iii-iv. doi: 10.3310/hta9210. Health Technol Assess. 2005. PMID: 15899149
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
Cited by
-
Antibody-mediated rejection-treatment standard.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2025 Aug 1;40(8):1615-1627. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfaf097. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2025. PMID: 40440205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shedding Light on Microvascular Inflammation: Understanding Outcomes, But What Sparks the Flame?Transpl Int. 2024 Nov 26;37:14032. doi: 10.3389/ti.2024.14032. eCollection 2024. Transpl Int. 2024. PMID: 39659965 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Targeting CD38 in Antibody-Mediated Rejection.Transpl Int. 2025 May 15;38:14343. doi: 10.3389/ti.2025.14343. eCollection 2025. Transpl Int. 2025. PMID: 40444214 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

