Astrocytes induce desynchronization and reduce predictability in neuron-astrocyte networks cultured on microelectrode arrays
- PMID: 39479242
- PMCID: PMC11521599
- DOI: 10.1098/rsos.240839
Astrocytes induce desynchronization and reduce predictability in neuron-astrocyte networks cultured on microelectrode arrays
Abstract
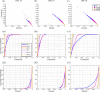
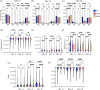
In this article, we aim to study how astrocytes control electrophysiological activity during neuronal network formation. We used a combination of spike/burst analysis, classification of spike waveforms based on various signal properties and tools from information theory to demonstrate how astrocytes modulate the electrical activity of neurons using microelectrode array (MEA) signals. We cultured rat primary cortical neurons and astrocytes on 60-electrode MEAs with different neuron/astrocyte ratios ranging from 'pure' neuronal cultures to co-cultures containing 50% neurons and 50% astrocytes. Our results show that astrocytes desynchronize the network and reduce predictability in the signals and affect the repolarization phase of the action potentials. Our work highlights that it is crucial to go beyond standard MEA analysis to assess how astrocytes control neuronal cultures and investigate any dysfunction that could potentially result in neuronal hyperactivity.
Keywords: astrocytes; ionic buffering; microelectrode arrays; neuronal networks; signal analysis.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Tan CX, Lane CJB, Eroglu C. 2021. Role of astrocytes in synapse formation and maturation. In Molecular mechanisms of neural development and insights into disease,current topics in developmental biology (ed. Bashaw GJ), pp. 371–407, vol. 142. Cambridge, MA: Academic Press. (10.1016/bs.ctdb.2020.12.010) - DOI - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

