Reporting ethical approval in case reports and case series in 12 consecutive years: A systematic review
- PMID: 39479275
- PMCID: PMC11520241
- DOI: 10.1002/hcs2.113
Reporting ethical approval in case reports and case series in 12 consecutive years: A systematic review
Abstract
Our study describes the reported rate of the Institutional Review Board (IRB) approval, declaration of Helsinki (DoH), and informed consent in the case reports and case series and investigates factors associated with the ethical approval report. We searched PubMed for case reports and case series from 2006 to 2017. Annually, we obtained the first 20 articles of a case report cluster from 20 distinct publications. This analysis initially contained at least 2400 papers, with 100 papers each study design and year. Only 26 (5.4%) of 480 included studies reported IRB approval, DoH approval, and participant informed consent; 58 (12.1%) reported two out of three ethical statements (DoH, informed consent, IRB); and 151 (31.5%) reported only one, leading to nearly 245 studies (51.0%) did not report any ethical approval item. Both clusters mentioned the DoH the least. Only years, ages, ethical item types, and cluster types were associated with ethical reporting practices. This study found the serious under-reporting of ethical practices in both case reports and case series.
Keywords: case report; case series; declaration of Helsinki; ethical approval; informed consent; institutional review board.
© 2024 The Author(s). Health Care Science published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Tsinghua University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
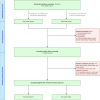
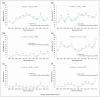
References
-
- McKenna L, Gray R. The importance of ethics in research publications. Collegian. 2018;25(2):147–148. 10.1016/j.colegn.2018.02.006 - DOI
-
- Department of Health, Education, and Welfare; National Commission for the Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioral Research . The Belmont report. Ethical principles and guidelines for the protection of human subjects of research. J Am Coll Dent. 2014;81(3):4–13. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25951677/ - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
