Revisiting the role of MicroRNAs in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 39479511
- PMCID: PMC11521927
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1470875
Revisiting the role of MicroRNAs in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
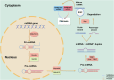
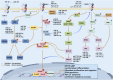
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a prevalent chronic pulmonary fibrosis disease characterized by alveolar epithelial cell damage, fibroblast proliferation and activation, excessive extracellular matrix deposition, and abnormal epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), resulting in tissue remodeling and irreversible structural distortion. The mortality rate of IPF is very high, with a median survival time of 2-3 years after diagnosis. The exact cause of IPF remains unknown, but increasing evidence supports the central role of epigenetic changes, particularly microRNA (miRNA), in IPF. Approximately 10% of miRNAs in IPF lung tissue exhibit differential expression compared to normal lung tissue. Diverse miRNA phenotypes exert either a pro-fibrotic or anti-fibrotic influence on the progression of IPF. In the context of IPF, epigenetic factors such as DNA methylation and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) regulate differentially expressed miRNAs, which in turn modulate various signaling pathways implicated in this process, including transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1)/Smad, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/AKT) pathways. Therefore, this review presents the epidemiology of IPF, discusses the multifaceted regulatory roles of miRNAs in IPF, and explores the impact of miRNAs on IPF through various pathways, particularly the TGF-β1/Smad pathway and its constituent structures. Consequently, we investigate the potential for targeting miRNAs as a treatment for IPF, thereby contributing to advancements in IPF research.
Keywords: IPF; MAPK; PI3K/AKT; TGF-β1/Smad; miRNA.
Copyright © 2024 Zhou, Xie, Wei, Zhang and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ESL attenuates BLM-induced IPF in mice: Dual mediation of the TLR4/NF-κB and TGF-β1/PI3K/Akt/FOXO3a pathways.Phytomedicine. 2024 Sep;132:155545. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155545. Epub 2024 Apr 2. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38972238
-
SULF1 expression is increased and promotes fibrosis through the TGF-β1/SMAD pathway in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.J Transl Med. 2024 Oct 1;22(1):885. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05698-3. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39354547 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, new research progress and their pathophysiological implication.Exp Lung Res. 2018 Apr;44(3):178-190. doi: 10.1080/01902148.2018.1455927. Epub 2018 Apr 23. Exp Lung Res. 2018. PMID: 29683754 Review.
-
Role of MicroRNAs in Signaling Pathways Associated with the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Focus on Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 14;23(12):6613. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126613. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35743055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deficiency of HtrA3 Attenuates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Via TGF-β1/Smad Signaling Pathway.Lung. 2023 Apr;201(2):235-242. doi: 10.1007/s00408-023-00608-8. Epub 2023 Feb 24. Lung. 2023. PMID: 36823409
Cited by
-
Recent progress in exosomal non-coding RNAs research related to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Front Genet. 2025 Mar 27;16:1556495. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1556495. eCollection 2025. Front Genet. 2025. PMID: 40212286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of glycolysis-related gene signatures for prognosis and therapeutic targeting in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 28;16:1486357. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1486357. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40093327 Free PMC article.
-
[Pathophysiology of fibrosis: inflammatory vs. non-inflammatory].Inn Med (Heidelb). 2025 Jul;66(7):659-665. doi: 10.1007/s00108-025-01890-9. Epub 2025 Apr 3. Inn Med (Heidelb). 2025. PMID: 40180658 Review. German.
-
Circulating MicroRNAs in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Narrative Review.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Dec 4;46(12):13746-13766. doi: 10.3390/cimb46120821. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39727949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Therapeutics for Chronic Lung Diseases: From Standard Therapies to Emerging Breakthroughs.J Clin Med. 2025 Apr 30;14(9):3118. doi: 10.3390/jcm14093118. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40364149 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bahudhanapati H., Tan J., Dutta J. A., Strock S. B., Sembrat J., Àlvarez D., et al. (2019). Microrna-144-3p targets relaxin/insulin-like family Peptide receptor 1 (Rxfp1) expression in lung fibroblasts from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Biol. Chem. 294 (13), 5008–5022. Epub 2019/02/03. 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004910 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bai J., Deng J., Han Z., Cui Y., He R., Gu Y., et al. (2021). Circrna_0026344 via exosomal mir-21 regulation of Smad7 is involved in aberrant cross-talk of epithelium-fibroblasts during cigarette smoke-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Toxicol. Lett. 347, 58–66. Epub 2021/05/08. 10.1016/j.toxlet.2021.04.017 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

