Novel formulations ameliorate osteoarthritis in rats by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress
- PMID: 39479600
- PMCID: PMC11521736
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.4407
Novel formulations ameliorate osteoarthritis in rats by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress
Abstract
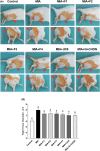
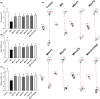
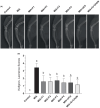
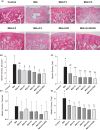
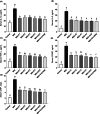
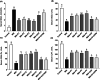
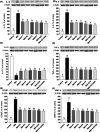
The study tested new oral plant-based formulations (F) on rats with monosodium iodoacetate (MIA)-induced osteoarthritis, measuring inflammation, antioxidant levels, paw size, stride, and analyzing knee joint images. Fifty-six female Sprague Dawley rats were allocated into 8 groups: (1) Control, (2) MIA (OA induced with MIA), (3) MIA + F1 [curcuminoids+gingerols+acetyl-11-keto-β boswellic acid (AKBA)], (4) MIA + F2 (curcuminoids+Withania glycosides+AKBA), (5) MIA + F3 (curcuminoids+total withanolides+AKBA), (6) MIA + F4 (curcuminoids, AKBA), (7) MIA + UCII (type II collagen), and (8) MIA + GCHON (Glucosamine Chondroitin). Treatments F1 to F4 reduced right joint diameter and improved stride length and paw area in OA rats. Despite improvements with treatments F1 to F4, there was no significant difference between these groups (p > .05). In OA animals, F1 to F4 treatments decreased MDA levels and increased antioxidant enzymes activities (p < .001). This was done by reducing levels of inflammatory markers and enzymes like IL-1β, IL-6, MMP-8, TNF-α, CRP, COMP, and LOX-5, while increasing the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10. In conclusion, these plant-based treatments significantly reduced osteoarthritis severity, slowed disease progression by reducing inflammation, and protected joints from damage, showing a protective effect in rats with induced osteoarthritis, likely due to their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Keywords: anti‐inflammatory; inflammation; osteoarthritis; oxidative stress; plant‐based formulations.
© 2024 The Author(s). Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Abhijeet Morde and Muralidhara Padigaru. are employees of OmniActive Health Technologies (Mumbai, India). The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abo‐Zalam, H. B. , Abdelsalam, R. M. , Abdel‐Rahman, R. F. , Abd‐Ellah, M. F. , & Khattab, M. M. (2021). In vivo investigation of the ameliorating effect of tempol against MIA‐induced knee osteoarthritis in rats: Involvement of TGF‐β1/SMAD3/NOX4 cue. Molecules, 26(22), 6993. 10.3390/molecules26226993 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abusarah, J. , Benabdoune, H. , Shi, Q. , Lussier, B. , Martel‐Pelletier, J. , Malo, M. , Fernandes, J. C. , de Souza, F. P. , Fahmi, H. , & Benderdour, M. (2017). Elucidating the role of protandim and 6‐gingerol in protection against osteoarthritis. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 118(5), 1003–1013. 10.1002/jcb.25659 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Catanzaro, D. , Rancan, S. , Orso, G. , Dall'Acqua, S. , Brun, P. , Giron, M. C. , Carrara, M. , Castagliuolo, I. , Ragazzi, E. , Caparrotta, L. , & Montopoli, M. (2015). Boswellia serrata preserves intestinal epithelial barrier from oxidative and inflammatory damage. PLoS One, 10(5), e0125375. 10.1371/journal.pone.0125375 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

