Performance of the LifeScale automated rapid phenotypic antimicrobial susceptibility testing on Gram-negative rods directly from positive blood cultures
- PMID: 39480069
- PMCID: PMC11633210
- DOI: 10.1128/jcm.00922-24
Performance of the LifeScale automated rapid phenotypic antimicrobial susceptibility testing on Gram-negative rods directly from positive blood cultures
Erratum in
-
Erratum for Snyder et al., "Performance of the LifeScale automated rapid phenotypic antimicrobial susceptibility testing on Gram-negative rods directly from positive blood cultures".J Clin Microbiol. 2025 Mar 12;63(3):e0015625. doi: 10.1128/jcm.00156-25. Epub 2025 Feb 12. J Clin Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39936894 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
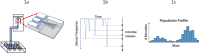
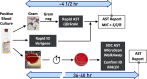
Rapid antimicrobial susceptibility testing (rAST) performed directly from blood cultures is essential to influencing the selection of appropriate antibiotics, preferably targeted therapy, for the treatment of bloodstream infections. Affinity Biosensors has developed the LifeScale, a phenotypic rAST system based on microfluidic sensors with a mechanical resonator that measures the mass of individual microbes. The combination of replication, biomass, and population profiling of individual microbes is analyzed to produce rAST results. The performance of the LifeScale was evaluated and compared to our current standard of care (SOC) antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) system under clinical conditions. The results indicated that the LifeScale is easy to use and provides rapid, reliable, and accurate AST results in less than 5 h directly from from positive blood cultures containing Gram-negative organisms listed in the current database. For all organism-antibiotic combinations involving polymicrobial cultures, LifeScale showed a resistant result when either mixed isolate was resistant. If these results prove to be robust on further testing, this may justify the reporting of rapid LifeScale results without the need for additional confirmatory testing.
Importance: This is the first clinical-based study of a unique technology using microfluidic sensors to generate rapid antimicrobial susceptibility test results directly from blood cultures containing Gram-negative rods. The issue of polymicrobial cultures was also addressed in this study, which, to our knowledge, has not been addressed in publications of other rapid phenotypic AST systems. Overall, LifeScale results compared favorably with the SOC in terms of overall agreement, especially categorical agreement.
Keywords: Gram stain; Gram-negative bacteria; MALDI-TOF; MicroScan; Verigene; antimicrobial stewarship; antimicrobial susceptibility testing; blood culutres; microfluidics; polymicrobial.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical