Performance of rapid antigen tests to detect SARS-CoV-2 variant diversity and correlation with viral culture positivity: implication for diagnostic development and future public health strategies
- PMID: 39480114
- PMCID: PMC11633148
- DOI: 10.1128/mbio.02737-24
Performance of rapid antigen tests to detect SARS-CoV-2 variant diversity and correlation with viral culture positivity: implication for diagnostic development and future public health strategies
Abstract
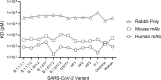
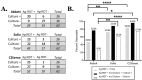
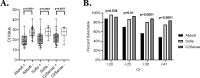
Antigen-based rapid diagnostic tests (Ag-RDTs) provide timely results, are simple to use, and are less expensive than molecular assays. Recent studies suggest that antigen-based testing aligns with virus culture-based results (a proxy of contagiousness at the peak viral phase of illness); however, the performance of Ag-RDTs for newer SARS-CoV-2 variants is unclear. In this study, we (i) assessed the performance of Ag-RDTs and diagnostic antibodies to detect a range of SARS-CoV-2 variants and (ii) determined whether Ag-RDT results correlated with culture positivity. We noted only minor differences in the limit of detection by variant for all assays, and we demonstrated consistent antibody affinity to the N protein among the different variants. We observed moderate to high sensitivity (46.8%-83.9%) for Ag-RDTs when compared to PCR positivity (100%), and all variants were assessed on each assay. Ag-RDT sensitivity and PCR Ct showed an inverse correlation with the detection of viable virus. Collectively, our results demonstrate that commercially available Ag-RDTs offer variable sensitivity compared to PCR, show similar diagnostic validity across variants, and may predict the risk of transmissibility. These findings may be used to support more tailored SARS-CoV-2 isolation strategies, particularly if other studies clarify the direct association between Ag-RDT positivity and transmission risk. The apparent trade-off between sensitivity in the detection of any PCR-positive infection and concordance with infectious virus positivity may also inform new RDT diagnostic development strategies for SARS-CoV-2 and other epidemic respiratory pathogens.
Importance: Despite the availability of vaccines, COVID-19 continues to be a major health concern, and antigen-based rapid diagnostic tests (Ag-RDTs) are commonly used as point-of-care or at-home diagnostic tests. In this study, we evaluated the performance of two commercially available Ag-RDTs and a research Ag-RDT to detect multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants using upper respiratory tract swab samples from clinical COVID-19 cases. Furthermore, we determined whether Ag-RDT results correlated with culture positivity, a potential proxy of viral transmissibility. Our results have important implications to inform future testing and response strategies during periods of high COVID-19 transmission with new variants.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; antigen-based rapid diagnostic tests; viral culture positivity.
Conflict of interest statement
J.C., R.D., and J.W. are employees of C2Sense, Inc., a company that designs and sells lateral flow assay readers. J.C., R.D., and J.W. were not directly involved in the laboratory or statistical analyses presented here. S.D.P. and M.P.S. report that the Uniformed Services University (USU) Infectious Diseases Clinical Research Program (IDCRP), a U.S. Department of Defense institution, and the Henry M. Jackson Foundation (HJF) were funded under a Cooperative Research and Development Agreement to conduct an unrelated phase III COVID-19 monoclonal antibody immunoprophylaxis trial sponsored by AstraZeneca. The HJF, in support of the USU IDCRP, was funded by the Department of Defense Joint Program Executive Office for Chemical, Biological, Radiological, and Nuclear Defense to augment the conduct of an unrelated phase III vaccine trial sponsored by AstraZeneca. Both of these trials were part of the U.S. Government COVID-19 response. Neither is related to the work presented here.
Figures

References
-
- Altarawneh HN, Chemaitelly H, Ayoub HH, Tang P, Hasan MR, Yassine HM, Al-Khatib HA, Al Thani AA, Coyle P, Al-Kanaani Z, Al-Kuwari E, Jeremijenko A, Kaleeckal AH, Latif AN, Shaik RM, Abdul-Rahim HF, Nasrallah GK, Al-Kuwari MG, Butt AA, Al-Romaihi HE, Al-Thani MH, Al-Khal A, Bertollini R, Abu-Raddad LJ. 2023. Effects of previous infection, vaccination, and hybrid immunity against symptomatic Alpha, Beta, and Delta SARS-CoV-2 infections: an observational study. EBioMedicine 95:104734. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104734 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
