Lnc-H19-derived protein shapes the immunosuppressive microenvironment of glioblastoma
- PMID: 39481387
- PMCID: PMC11604490
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101806
Lnc-H19-derived protein shapes the immunosuppressive microenvironment of glioblastoma
Erratum in
-
Lnc-H19-derived protein shapes the immunosuppressive microenvironment of glioblastoma.Cell Rep Med. 2025 Mar 18;6(3):101993. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.101993. Epub 2025 Feb 13. Cell Rep Med. 2025. PMID: 39952237 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
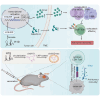
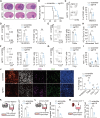
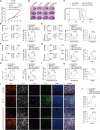
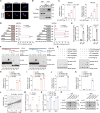
The immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) is a prominent feature of glioblastoma (GBM), the most lethal primary brain cancer resistant to current immunotherapies. The mechanisms underlying GBM-TME remain to be explored. We report that long non-coding RNA (LncRNA) H19 encodes an immune-related protein called H19-IRP. Functionally separated from H19 RNA, H19-IRP promotes GBM immunosuppression by binding to the CCL2 and Galectin-9 promoters and activating their transcription, thereby recruiting myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), leading to T cell exhaustion and an immunosuppressive GBM-TME. H19-IRP, overexpressed in clinical GBM samples, acts as a tumor-associated antigen (TAA) presented by major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I). A circular RNA vaccine targeting H19-IRP (circH19-vac) triggers a potent cytotoxic T cell response against GBM and inhibits GBM growth. Our results highlight the unrevealed function of H19-IRP in creating immunosuppressive GBM-TME by recruiting MDSCs and TAMs, supporting the idea of targeting H19-IRP with cancer vaccine for GBM treatment.
Keywords: GBM; H19; H19-IRP; LncRNA; TME; circular RNA vaccine; immunotherapy.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Topalian S.L., Hodi F.S., Brahmer J.R., Gettinger S.N., Smith D.C., McDermott D.F., Powderly J.D., Carvajal R.D., Sosman J.A., Atkins M.B., et al. Safety, Activity, and Immune Correlates of Anti–PD-1 Antibody in Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012;366:2443–2454. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1200690. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

