Circular RNA landscape in extracellular vesicles from human biofluids
- PMID: 39482783
- PMCID: PMC11526565
- DOI: 10.1186/s13073-024-01400-w
Circular RNA landscape in extracellular vesicles from human biofluids
Abstract
Background: Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have emerged as a prominent class of covalently closed single-stranded RNA molecules that exhibit tissue-specific expression and potential as biomarkers in extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from liquid biopsies. Still, their characteristics and applications in EVs remain to be unveiled.
Methods: We performed a comprehensive analysis of EV-derived circRNAs (EV-circRNAs) using transcriptomics data obtained from 1082 human body fluids, including plasma, urine, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and bile. Our validation strategy utilized RT-qPCR and RNA immunoprecipitation assays, complemented by computational techniques for analyzing EV-circRNA features and RNA-binding protein interactions.
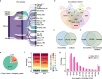
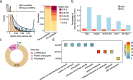
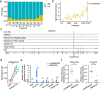
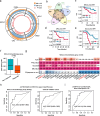
Results: We identified 136,327 EV-circRNAs from various human body fluids. Significantly, a considerable amount of circRNAs with a high back-splicing ratio are highly enriched in EVs compared to linear RNAs. Additionally, we discovered brain-specific circRNAs enriched in plasma EVs and cancer-associated EV-circRNAs linked to clinical outcomes. Moreover, we demonstrated that EV-circRNAs have the potential to serve as biomarkers for evaluating immunotherapy efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Importantly, we identified the involvement of RBPs, particularly YBX1, in the sorting mechanism of circRNAs into EVs.
Conclusions: This study unveils the extensive repertoire of EV-circRNAs across human biofluids, offering insights into their potential as disease biomarkers and their mechanistic roles within EVs. The identification of specific circRNAs and the elucidation of RBP-mediated sorting mechanisms open new avenues for the clinical application of EV-circRNAs in disease diagnostics and therapeutics.
Keywords: Biomarker; Cancer; Circular RNAs; Extracellular vesicles; RNA-binding proteins.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Liu CX, Chen LL. Circular RNAs: Characterization, cellular roles, and applications. Cell. 2022;185(12):2016–34. 10.1016/j.cell.2022.04.021. - PubMed
-
- Kristensen LS, Jakobsen T, Hager H, Kjems J. The emerging roles of circRNAs in cancer and oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2022;19(3):188–206. 10.1038/s41571-021-00585-y. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

