Correlation between circulating dephosphorylated uncarboxylated matrix Gla protein and vascular calcification in peritoneal dialysis patients
- PMID: 39482813
- PMCID: PMC11613520
- DOI: 10.1177/03913988241293980
Correlation between circulating dephosphorylated uncarboxylated matrix Gla protein and vascular calcification in peritoneal dialysis patients
Abstract
Introduction: To explore the association between serum Dephosphorylated uncarboxylated matrix Gla protein (dp-ucMGP) and abdominal aortic calcification (AAC) in peritoneal dialysis (PD) patients.
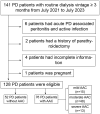
Methods: A total 128 PD patients and 120 healthy controls were enrolled into the study. Serum dp-ucMGP was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Abdominal lateral plain radiography was used to evaluate the abdominal aortic calcification score (AACS). PD patients were divided into two groups according to the presence or absence of AAC. The relationships between dp-ucMGP levels and AACS were assessed by Spearman analysis and the value of dp-ucMGP in predicting AAC was evaluated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC).
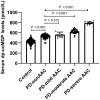
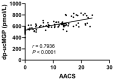
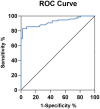
Results: Serum dp-ucMGP in PD patients were significantly higher than controls (p < 0.05). And PD patients with AAC had higher serum dp-ucMGP than that of PD patients without AAC (p < 0.05). The serum dp-ucMGP levels was positively associated with AACS (r = 0.794, p < 0.0001) in PD patients. The multivariate logistic regression analyses showed that serum dp-ucMGP was independent factors of AAC in PD patients (OR = 2.555, 95% CI = 1.415-4.609). The area under ROC curve of dp-ucMGP was 0.9227, the corresponding sensitivity was 0.86, and the specificity was 0.92.
Conclusion: Serum dp-ucMGP levels were positively associated with the AACS in PD patients. Higher serum dp-ucMGP level is independently associated with AAC in PD patients.
Keywords: Peritoneal dialysis; abdominal aortic calcification; dephosphorylated uncarboxylated matrix Gla protein; vascular calcification.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Liabeuf S, Okazaki H, Desjardins L, et al. Vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease: are biomarkers useful for probing the pathobiology and the health risks of this process in the clinical scenario? Nephrol Dial Transplant 2014; 29: 1275–1284. - PubMed
-
- Price PA, Urist MR, Otawara Y. Matrix Gla protein, a new gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing protein which is associated with the organic matrix of bone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1983; 117: 765–771. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

