Novel management of pseudomonas biofilm-like structure in a post-pneumonectomy empyema
- PMID: 39483118
- PMCID: PMC11525003
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1458652
Novel management of pseudomonas biofilm-like structure in a post-pneumonectomy empyema
Abstract
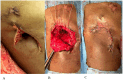
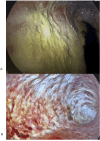
We present a patient with a post-pneumonectomy empyema refractory to surgical debridement and systemic antibiotics. The patient initially presented with a bronchopleural fistula and pneumothorax secondary to tuberculosis (TB) destroyed lung, which required a pneumonectomy with Eloesser flap. Ongoing pleural infection delayed the closure of the Eloesser flap, and thoracoscopic inspection of his chest cavity revealed a green, mucous biofilm-like structure lining the postpneumonectomy pleural cavity. Cultures identified pan-susceptible Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Despite debriding this biofilm-like structure and administering systemic antibiotics, the patient continued to show persistent signs of infection and regrowth of the film. We employed a novel approach to dissolve the biofilm-like structure using intrapleural dornase alfa followed by intrapleural antibiotic washes. After 3 weeks of daily washes, repeat inspection demonstrated the biofilm-like structure had completely resolved. Resolving the pseudomonas biofilm-like structure allowed permanent closure of his chest without further need for systemic antibiotics. At follow up 3 months later, he showed no sequalae. This treatment option can be an important adjunct to improve likelihood of chest closure in patients with post-pneumonectomy empyema that resists standard treatment options due to biofilm formation.
Keywords: alfa; biofilm-like structure; dornase; empyema; pneumonectomy; pseudomonas; tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2024 Gustafson, Larrain, Friedman, Repkorwich, Anidi, Forrest, Fennelly and Carr.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Azevedo I., Oliveira R. L., Ugalde P. A. (2020). Management of postpneumonectomy empyema and bronchopleural fistula. Shanghai Chest. 5. doi: 10.21037/shc.2020.03.11 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

