This is a preprint.
HIV persists in late coronary atheroma and is associated with increased local inflammation and disease progression
- PMID: 39483879
- PMCID: PMC11527356
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5125826/v1
HIV persists in late coronary atheroma and is associated with increased local inflammation and disease progression
Abstract
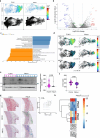
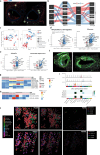
Chronic inflammation contributes to the prevalence of cardiovascular disease in people living with HIV (PLWH). The immune mechanisms driving atherosclerosis progression in PLWH remain unclear. This study conducted comprehensive assessments of medium-sized coronary arteries and aorta from deceased PLWH and controls without HIV using DNA/RNA assays, spatial transcriptomics, and high-resolution mass spectrometry. Findings revealed more significant inflammation correlated with higher HIV copy numbers in late atheroma of PLWH. Enhanced CXCL12 and decreased ABCA1/ABCG1 expression in CD163+ macrophages were co-localized in coronaries of PLWH, suggesting a reduction in plasma lipoprotein clearance compared to controls. Spatial analyses identified potential therapeutic targets by revealing inflammatory changes in medium-sized arteries and the aorta. We examined the relationship between atherosclerotic phenotypes and inflammatory gene expression in Vanderbilts Biobank to study these findings in a larger clinical cohort. This established a significant association between ABCA1 and CXCL12 gene expressions with atherosclerosis, partly influenced by HIV.
Keywords: ABCA1; Atherosclerosis; CD163; CXCL12; HIV; cardiovascular disease.
Figures




References
-
- Currier J.S., et al. Coronary heart disease in HIV-infected individuals. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 33, 506–512 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000445/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL159351/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI170228/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 HL065962/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR025141/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA057204/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R25 HL106365/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD074711/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM115305/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006378/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R25 AI164610/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD017985/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI136740/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD023475/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI164559/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 GM092618/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI110527/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS032830/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004798/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL156759/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002243/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

