This is a preprint.
Neural network analysis as a novel skin outcome in a trial of belumosudil in patients with systemic sclerosis
- PMID: 39483897
- PMCID: PMC11527259
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4889334/v1
Neural network analysis as a novel skin outcome in a trial of belumosudil in patients with systemic sclerosis
Update in
-
Neural network analysis as a novel skin outcome in a trial of belumosudil in patients with systemic sclerosis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2025 Apr 11;27(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s13075-025-03508-9. Arthritis Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40217251 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: The modified Rodnan skin score (mRSS), used to measure dermal thickness in patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc), is agnostic to inflammation and vasculopathy. Previously, we demonstrated the potential of neural network-based digital pathology applied to stained skin biopsies from SSc patients as a quantitative outcome. We leveraged deep learning and histologic analyses of clinical trial biopsies to decipher SSc skin features 'seen' by artificial intelligence (AI).
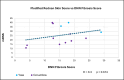
Methods: Adults with diffuse cutaneous SSc (disease duration ≤ 6 years) enrolled in an open-label trial evaluating belumosudil underwent serial mRSS assessment and dorsal arm biopsies at week 0, 24 and 52/end of trial. Two blinded dermatopathologists independently scored stained sections [Masson's trichrome, hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), CD3, CD34, CD8, α smooth muscle actin (αSMA)] for 16 published SSc dermal pathological parameters. We applied our previously published deep learning model to generate QIF signatures/biopsy and generated Fibrosis Scores. Associations between Fibrosis Score and mRSS (Spearman correlation); and between Fibrosis Score mRSS versus histologic parameters [odds ratios (OR)] were determined.
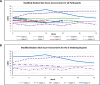
Results: Only ten patients were enrolled because the sponsor terminated the trial early. Median, interquartile range (IQR) for mRSS change (0-52 weeks) for the five participants with paired biopsies was - 2.5 (-11-7.5), and for the ten participants was - 2 (-9-7.5). The correlation between Fibrosis Score and mRSS was R = 0.3; p = 0.674. Per 1-unit mRSS change (0-52W), histologic parameters with the greatest associated changes were (OR, p-value): telangiectasia (2.01, 0.001), perivascular CD3+ (1.03, 0.015), and % of CD8 + among CD3+ (1.08, 0.031). Likewise, per 1-unit Fibrosis Score change, parameters with greatest changes were (OR, p-value): hyalinized collagen (1.1, < 0.001), subcutaneous (SC) fat loss (1.47, < 0.001), thickened intima (1.21, 0.005), and eccrine entrapment (1.14, 0.046).
Conclusions: Belumosudil was associated with a non-clinically meaningful improvement in mRSS. Fibrosis Score changes correlated with histologic feature changes (e.g., hyalinized collagen, SC fat loss) that were distinct from those associated with mRSS changes (e.g., telangiectasia, perivascular CD3+, and % of CD8 + among CD3+). These data suggest that AI applied to SSc biopsies may be useful for quantifying pathologic features of SSc beyond skin thickness.
Keywords: AlexNet; Deep Neural Network; artificial intelligence; belumosudil; dermal fibrosis; modified Rodnan skin score; outcome measure; outcomes; scleroderma; skin fibrosis; systemic sclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests MH has received consultancy fees from AbbVie and has received research grant support from Boehringer Ingelheim for an investigator-initiated research project. She is a Scientific Advisory Board Member for the Scleroderma Foundation. She has participated in clinical trials. EJB has received research grants from Kadmon, Boehringer Ingelheim and aTyr. EV has received consulting fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, GSK, Abbvie, BMS, and GLG, has received support from Boehringer Ingelheim, Horizon, Prometheus, Kadmon, and GSK, and serves on the advisory board for Cabaletta and Boehringer Ingelheim. FPW reports research support from AHRQ (R01HS027626), Amgen, and Whoop. FPW reports consulting for Hekaheart, Aura Care, and WndrHlth.
Figures



References
-
- Hughes M., et al. , MRI Digital Artery Volume Index (DAVIX) as a surrogate outcome measure of digital ulcer disease in patients with systemic sclerosis: a prospective cohort study. Lancet Rheumatol, 2023. 5(10): p. e611–e621. - PubMed
-
- LeRoy E.C., et al. , Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis): classification, subsets and pathogenesis. J Rheumatol, 1988. 15(2): p. 202–5. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

