Fluoride effect on renal and hepatic functions: A comprehensive decade review of In vitro and In vivo studies
- PMID: 39484005
- PMCID: PMC11525447
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2024.10.002
Fluoride effect on renal and hepatic functions: A comprehensive decade review of In vitro and In vivo studies
Abstract
Background: This systematic review evaluates the toxicological effects of exposure to fluoride on renal and hepatic functioning. It compiles both in vitro & in vivo studies across the last decade. By highlighting the potential health risks, the review aims to raise awareness and encourage a more attentive approach to fluoride use and exposure, instilling a sense of concern and vigilance in the audience.
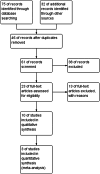
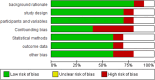
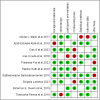
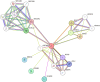
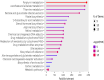
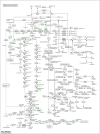
Methodology: A thorough literature search covered relevant studies from 2013 to 2023, both experimental (in vitro) and animal (in vivo) research. The data extraction process focused on critical aspects such as sample size, methodologies used, key findings, and conclusions regarding fluoride's impact on kidney and liver functions. The review also includes a detailed analysis of gene expression, KEGG pathways, and STRING analysis, further enhancing the reliability of the results.
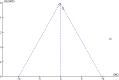
Results: Significant renal and liver damage were demonstrated in animal models exposed to high fluoride doses for long duration. Ferulic acid was found to mitigate fluoride-induced oxidative damage. The combined mean difference across studies was 6.52 [-5.22, 18.26], indicating high heterogeneity, which reflects diverse methodologies and findings. Notably, epigenetic and immune system impacts were underscored, with gene analysis identifying several genes involved in oxidative stress response, apoptosis, and inflammation pathways.
Conclusion: The findings emphasize the substantial evidence of its harmful effects on renal and liver functions at high exposure levels. Some studies indicate minimal impact, others demonstrate significant organ damage. The results underline the necessity for continued research to establish safe fluoride exposure limits and comprehend the mechanisms underlying its toxicity.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
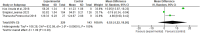
Similar articles
-
Dietary glycation compounds - implications for human health.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2024 Sep;54(8):485-617. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2024.2362985. Epub 2024 Aug 16. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39150724
-
Understanding the Early Biological Effects of Isoprene-Derived Particulate Matter Enhanced by Anthropogenic Pollutants.Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 2019 Mar;2019(198):1-54. Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 2019. PMID: 31872748 Free PMC article.
-
Deployment of personnel to military operations: impact on mental health and social functioning.Campbell Syst Rev. 2018 Jun 1;14(1):1-127. doi: 10.4073/csr.2018.6. eCollection 2018. Campbell Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 37131363 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorative effect of traditional polyherbal formulation on TNF-α, IL-1β and Caspase-3 expression in kidneys of wistar rats against sodium fluoride induced oxidative stress.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jan 10;318(Pt A):116900. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116900. Epub 2023 Jul 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37442489
-
Effects of fluoride exposure on mitochondrial function: Energy metabolism, dynamics, biogenesis and mitophagy.Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2022 Aug;94:103916. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2022.103916. Epub 2022 Jun 20. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35738460 Review.
References
-
- Shanmugam T., Selvaraj M. IntechOpen; 2022. Sources of Human Overexposure to Fluoride, its Toxicities, and Their Amelioration Using Natural Antioxidants [Internet]. Fluoride. - DOI
-
- Quadri Javed A., Alam M.M., Sarwar S., Singh S., Shariff A. Fluoride induced nephrotoxicity: apoptosis, ultrastructural changes and renal tubular injury in experimental animals. Int J Ayu Pharm Res [Internet] 2016 Sep.2;4(8) https://www.ijapr.in/index.php/ijapr/article/view/466 Available from:
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

