This is a preprint.
Immunogenic shift of arginine metabolism triggers systemic metabolic and immunological reprogramming to prevent HER2+ breast cancer
- PMID: 39484369
- PMCID: PMC11527010
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.10.23.619827
Immunogenic shift of arginine metabolism triggers systemic metabolic and immunological reprogramming to prevent HER2+ breast cancer
Update in
-
Immunogenic shift of arginine metabolism triggers systemic metabolic and immunological reprogramming to suppress HER2 + breast cancer.Cancer Metab. 2025 Mar 20;13(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s40170-025-00384-4. Cancer Metab. 2025. PMID: 40114277 Free PMC article.
Abstract
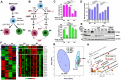
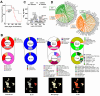
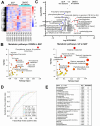
Arginine metabolism in tumors is often shunted into the pathway producing pro-tumor and immune suppressive polyamines (PAs), while downmodulating the alternative nitric oxide (NO) synthesis pathway. Aiming to correct arginine metabolism in tumors, arginine deprivation therapy and inhibitors of PA synthesis have been developed. Despite some therapeutic advantages, these approaches have often yielded severe side effects, making it necessary to explore an alternative strategy. We previously reported that supplementing SEP, the endogenous precursor of BH4 (the essential NO synthase cofactor), could correct arginine metabolism in tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and induce their metabolic and phenotypic reprogramming. We saw that oral SEP treatment effectively suppressed the growth of HER2-positive mammary tumors in animals. SEP also has no reported dose-dependent toxicity in clinical trials for metabolic disorders. In the present study, we report that a long-term use of SEP in animals susceptible to HER2-positive mammary tumors effectively prevented tumor occurrence. These SEP-treated animals had undergone reprogramming of the systemic metabolism and immunity, elevating total T cell counts in the circulation and bone marrow. Given that bone marrow-resident T cells are mostly memory T cells, it is plausible that chronic SEP treatment promoted memory T cell formation, leading to a potent tumor prevention. These findings suggest the possible roles of the SEP/BH4/NO axis in promoting memory T cell formation and its potential therapeutic utility for preventing HER2-positive breast cancer.
Keywords: HER2; T cells; arginine; breast cancer; cancer prevention; metabolism; nitric oxide; polyamines.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and competing interests statement The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Tapiero H, Mathé G, Couvreur P, Tew KD. I. Arginine. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2002;56(9):439–45. - PubMed
-
- Bauer PM, Buga GM, Fukuto JM, Pegg AE, Ignarro LJ. Nitric oxide inhibits ornithine decarboxylase via S-nitrosylation of cysteine 360 in the active site of the enzyme. J Biol Chem 2001;276(37):34458–64. - PubMed
-
- Tenu JP, Lepoivre M, Moali C, Brollo M, Mansuy D, Boucher JL. Effects of the new arginase inhibitor N(omega)-hydroxy-nor-L-arginine on NO synthase activity in murine macrophages. Nitric Oxide 1999;3(6):427–38. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
