This is a preprint.
Regulation of Sex-biased Gene Expression by the Ancestral X-Y Chromosomal Gene Pair Kdm5c-Kdm5d
- PMID: 39484414
- PMCID: PMC11527134
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.10.24.620066
Regulation of Sex-biased Gene Expression by the Ancestral X-Y Chromosomal Gene Pair Kdm5c-Kdm5d
Abstract
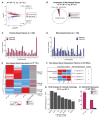
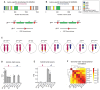
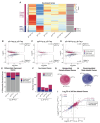
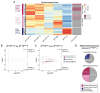
Conventionally, Y-linked Sry is thought to drive sex differences by triggering differential hormone production. Ancestral X-Y gene pairs, however, are hypothesized to drive hormone-independent sex differences. Here, we show that the X-Y gene pair Kdm5c-Kdm5d regulates sex-biased gene expression in pluripotent mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs). Wild-type (WT) XX female ESCs exhibit >2-fold higher expression of 409 genes relative to WT XY male ESCs. Conversely, WT XY male ESCs exhibit >2-fold higher expression of 126 genes compared to WT XX female ESCs. Loss of Kdm5c in female ESCs downregulates female-biased genes. In contrast, loss of either Kdm5c or Kdm5d in male ESCs upregulates female-biased genes and downregulates male-biased genes, effectively neutralizing sex-biased gene expression. KDM5C promotes the expression of Kdm5d and several other Y-linked genes in male ESCs. Moreover, ectopic Kdm5d expression in female ESCs is sufficient to drive male-biased gene expression. These results establish Kdm5c-Kdm5d as critical regulators of sex-biased gene expression.
Keywords: Embryonic stem cells; Pluripotency; Sex chromosomes; Sex differences; X-Y gene pairs.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests S.I. is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board of KDM5C Advocacy, Research, Education & Support (KARES). The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Blencowe M., Chen X., Zhao Y., Itoh Y., McQuillen C.N., Han Y., Shou B.L., McClusky R., Reue K., Arnold A.P., and Yang X. (2022). Relative contributions of sex hormones, sex chromosomes, and gonads to sex differences in tissue gene regulation. Genome Res 32, 807–824. 10.1101/gr.275965.121. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
