Transarterial chemoembolization combined with molecular targeted agents plus immune checkpoint inhibitors for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma beyond the up-to-seven criteria: a propensity score-matching analysis
- PMID: 39484705
- PMCID: PMC11536643
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2419993
Transarterial chemoembolization combined with molecular targeted agents plus immune checkpoint inhibitors for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma beyond the up-to-seven criteria: a propensity score-matching analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Not all patients benefit from transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) due to the heterogeneity of the tumour burden in intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). To compare the outcomes of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) combined with molecular-targeted agents plus immune checkpoint inhibitors (TACE-MTAs-ICIs) with those of TACE for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC) that were beyond the up-to-seven criteria.
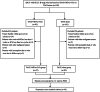
Patients and methods: Between January 2019 and July 2022, 130 patients diagnosed with uHCC beyond the up-to-seven criteria were retrospectively identified, including 47 patients who received TACE-MTAs-ICIs and 83 patients who received TACE alone. The primary endpoints were overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS); the secondary endpoints included tumour response and adverse events (AEs).
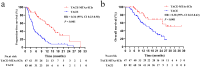
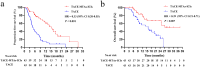
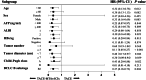
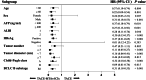
Results: There were 43 matched patients. The median OS and PFS times in the TACE-MTAs-ICIs group were significantly longer than those in the TACE group (OS: 27.2 vs. 15.9 months, p = 0.007; PFS: 15.4 months vs. 4.8 months, p < 0.001). The objective response rate (ORR) in the TACE-MTAs-ICIs group was higher than that in the TACE group (65.1% vs. 37.2%, p = 0.010). Reversible AEs (grade 3 or 4) occurred differently in TACE-MTAs-ICIs and TACE groups (83.7% vs. 51.2%, p = 0.001). Univariate and multivariate analyses revealed that TACE-MTAs-ICIs treatment was an independent favourable prognostic factor for both PFS and OS (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: For uHCC patients beyond the up-to-seven criteria, TACE-MTAs-ICIs provided superior ORR and OS. Early combined TACE and systemic treatment should shift for patients who are beyond these criteria.
Keywords: Carcinoma; chemoembolization; hepatocellular; immune checkpoint inhibitors; molecular-targeted therapy; therapeutic.
Plain language summary
The ORR and median OS reached 65.1% and 27.2 months, respectively, in the treatment model of TACE-MTAs-ICIs for patients with unresectable HCC that were beyond the up-to-seven criteria.TACE-TKI-ICI yielded a synergistic effect on these patients and was an independent favourable prognostic factor for PFS and OS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the article.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
