Berberine safeguards sepsis-triggered acute gastric damage and inhibits pyroptosis in gastric epithelial cells via suppressing the ubiquitination and degradation of Nrf2
- PMID: 39484787
- PMCID: PMC11895072
- DOI: 10.1002/kjm2.12900
Berberine safeguards sepsis-triggered acute gastric damage and inhibits pyroptosis in gastric epithelial cells via suppressing the ubiquitination and degradation of Nrf2
Abstract
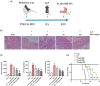
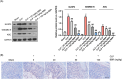
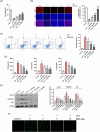
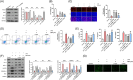
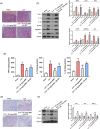
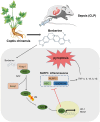
Berberine (BBR), a widely recognized traditional Chinese medicine, has attracted considerable attention for its promising anti-inflammatory effects. The activation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) effectively safeguards against organ damage stemming from sepsis-induced oxidative stress and inflammatory responses. This study examined the potential of BBR in alleviating sepsis-induced acute gastric injury, with a particular focus on elucidating whether its mechanism of action involves the activation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Following intraperitoneal injection of BBR, mice were subjected to the cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) method to induce sepsis. In vitro experiments involved pre-treating the normal gastric epithelial cells (GES-1) with BBR, followed by treatment with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Functional assays were then performed to assess cell proliferation and apoptosis. To validate the role of Nrf2 in pyroptosis and inflammation, siRNA targeting Nrf2 (si-Nrf2) was transfected into LPS-treated GES-1 cells. Additionally, mice were administered the Nrf2 inhibitor ML385 to confirm the protective effects of BBR in vivo. BBR displayed a dose-dependent effect in mitigating gastric tissue damage, suppressing the release of inflammatory cytokines, and reducing the expression of NLRP3, ASC, and GSDMD-N. In vitro, BBR fostered GES-1 cell proliferation, hindered apoptosis, and suppressed the levels of TNF-α, IL-18, IL-1β, NLRP3, ASC, and GSDMD-N. Further analysis revealed that knocking down Nrf2 reversed BBR's inhibitory effect on pyroptosis in LPS-treated GES-1 cells. Through binding to Keap1, BBR efficiently prevented the ubiquitination and degradation of Nrf2, ultimately promoting its nuclear translocation. In vivo experiments confirmed that ML385 reversed the protective effect of BBR on pyroptosis and inflammation. Our research reveals that BBR interacts with Keap1 to activate the Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway in gastric epithelial cells, thereby suppressing pyroptosis and inflammation in sepsis-induced acute gastric injury.
Keywords: Nrf2; acute gastric injury; berberine; inflammation; pyroptosis; sepsis.
© 2024 The Author(s). The Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Kaohsiung Medical University.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
LncRNA GAS5 inhibits miR-579-3p to activate SIRT1/PGC-1α/Nrf2 signaling pathway to reduce cell pyroptosis in sepsis-associated renal injury.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021 Jul 1;321(1):C117-C133. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00394.2020. Epub 2021 May 19. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34010066
-
New insights into evodiamine attenuates IPEC-J2 cells pyroptosis induced by T-2 toxin - Activating Keap1-Nrf2/NF-κB signaling pathway through binding with Keap1.J Environ Manage. 2024 Nov;370:122605. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.122605. Epub 2024 Sep 20. J Environ Manage. 2024. PMID: 39305878
-
Oxycodone attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial injury by inhibiting inflammation, oxidation and pyroptosis via Nrf2/HO-1 signalling pathway.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2024 Sep;51(9):e13910. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.13910. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39073215
-
The molecular mechanism of berberine affecting psoriasis skin inflammation by regulating keratinocyte pyroptosis via the p38 MAPK/NF-κB pathway.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr;398(4):3843-3859. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03461-5. Epub 2024 Oct 4. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39365309
-
Berberine Alleviates the Damage, Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction of PC12 Cells Induced by High Glucose by Activating the KEAP1/Nrf2/ARE Pathway.Mol Biotechnol. 2023 Oct;65(10):1632-1643. doi: 10.1007/s12033-022-00651-5. Epub 2023 Feb 3. Mol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36737555
Cited by
-
Dexmedetomidine Promotes Angiogenesis After Ischemic Stroke Through the NRF2/HO-1/VEGF Pathway.Neurochem Res. 2025 Apr 9;50(2):138. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04394-y. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40202562
References
-
- Leise BS, Fugler LA. Laminitis updates: sepsis/systemic inflammatory response syndrome‐associated laminitis. Vet Clin North Am Equine Pract. 2021;37(3):639–656. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

