A Core-Brush Nanoplatform with Enhanced Lubrication and Anti-Inflammatory Properties for Osteoarthritis Treatment
- PMID: 39484792
- PMCID: PMC11653621
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202406027
A Core-Brush Nanoplatform with Enhanced Lubrication and Anti-Inflammatory Properties for Osteoarthritis Treatment
Abstract
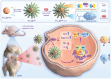
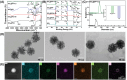
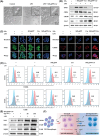
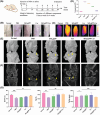
Osteoarthritis (OA) is recognized as a highly friction-related joint disease primarily associated with increased joint friction and inflammation due to pro-inflammatory M1-type macrophage infiltration in the articular cavity. Therefore, strategies to simultaneously increase lubrication and relieve inflammation to remodel the damaged articular microenvironment are of great significance for enhancing its treatment. Herein, a multifunctional core-brush nanoplatform composed of a ROS-scavenging polydopamine-coated SiO2 core and lubrication-enhancing zwitterionic poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine) (PMPC) brush and loaded with the anti-inflammatory drug curcumin by a reactive oxygen species (ROS)-liable conjugation (named as SiO2@PP-Cur) is rationally designed. Benefiting from the grafted zwitterionic PMPC brush, a tenacious hydration layer with enhanced lubricity for reducing joint abrasions is developed. More importantly, based on the mono-iodoacetic acid-induced arthritis (MIA) rat model, intra-articular injection of SiO2@PP-Cur nanoplatform can effectively alleviate articular inflammation via promoting macrophage polarization from the pro-inflammatory M1 to anti-inflammatory M2 state by activating the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) signaling pathway and attenuating the degradation of cartilage matrix, resulting in the remodeling of the damaged microenvironment into a pro-regenerative microenvironment. As a result, SiO2@PP-Cur can considerably inhibit OA progression. Therefore, the work may provide a novel strategy for the development of an advanced core-brush nanoplatform for enhanced OA therapy.
Keywords: controlled release; drug delivery; enhanced lubrication; inflammatory regulation; osteoarthritis.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Han Z., Bai L., Zhou J., Qian Y., Tang Y., Han Q., Zhang X., Zhang M., Yang X., Cui W., Hao Y., Biomaterials. 2022, 285, 121545. - PubMed
-
- Bruno M. C., Cristiano M. C., Celia C., d'Avanzo N., Mancuso A., Paolino D., Wolfram J., Fresta M., ACS Nano. 2022, 16, 19665. - PubMed
-
- Qiu W., Zhao W., Zhang L., Wang H., Li N., Chen K., Zhang H., Wang Y., Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2208189.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 92068119/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 22076104/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- ZR2021QE112/Fund for Natural Science Foundation of Shandong province
- ZR2024MB043/Fund for Natural Science Foundation of Shandong province
- tsqn202103105/Taishan Scholar Foundation of Shandong Province
- DFL20220401/Beijing Hospitals Authority's Plan
- JYY2023-11/Beijing Municipal Public Welfare Development and Reform Pilot Project for Medical Research Institutes
- JYY2023-8/Beijing Municipal Public Welfare Development and Reform Pilot Project for Medical Research Institutes
- BJRITO-RDP-2024/Beijing Municipal Health Commission
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
