Dynamic Evolution of Fibroblasts Revealed by Single-Cell RNA Sequencing of Human Pancreatic Cancer
- PMID: 39485038
- PMCID: PMC11609929
- DOI: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-23-0489
Dynamic Evolution of Fibroblasts Revealed by Single-Cell RNA Sequencing of Human Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
Abstract: Cancer progression and response to therapy are inextricably reliant on the coevolution of a supportive tissue microenvironment. This is particularly evident in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, a tumor type characterized by expansive and heterogeneous stroma. Herein, we employed single-cell RNA sequencing and spatial transcriptomics of normal, inflamed, and malignant pancreatic tissues to contextualize stromal dynamics associated with disease and treatment status, identifying temporal and spatial trajectories of fibroblast differentiation. Using analytical tools to infer cellular communication, together with a newly developed assay to annotate genomic alterations in cancer cells, we additionally explored the complex intercellular networks underlying tissue circuitry, highlighting a fibroblast-centric interactome that grows in strength and complexity in the context of malignant transformation. Our study yields new insights on the stromal remodeling events favoring the development of a tumor-supportive microenvironment and provides a powerful resource for the exploration of novel points of therapeutic intervention in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Significance: Pancreatic cancer remains a high unmet medical need. Understanding the interactions between stroma and cancer cells in this disease may unveil new opportunities for therapeutic intervention.
©2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
J. Chang reports personal fees from Novartis outside the submitted work. K. Lage reports being a consultant to ZS Associates and Sidera Bio and an equity holder in Sidera Bio, none of these roles are relevant to the work published here. G. Li reports employment with Novartis. D.T. Ting reports personal fees and other from ROME Therapeutics and PanTher Therapeutics, other from TellBio Inc., and ImproveBio Inc., personal fees from Moderna, Ikena Oncology, Sonata Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, abrdn, and Tekla Capital, and grants from Sanofi, Ava Therapeutics, Incyte Pharmaceuticals, and Astellas outside the submitted work. A.L. Grauel reports personal fees from Novartis Institutes for Biomedical Research during the conduct of the study. J.P. Wagner reports personal fees from Novartis during the conduct of the study, as well as other from Novartis outside the submitted work. G. Dranoff reports other from Novartis Pharmaceuticals during the conduct of the study, as well as other from Novartis Pharmaceuticals outside the submitted work. J.A. Engelman reports being an employee and equity holder of Treeline Biosciences. R. Leary reports personal fees from Novartis during the conduct of the study, as well as being a Novartis shareholder. A.S. Liss reports grants from Novartis and NIH during the conduct of the study, as well as other from Flare Therapeutics outside the submitted work. V. Cremasco reports personal fees from Novartis during the conduct of the study, as well as personal fees from Novartis outside the submitted work. No disclosures were reported by the other authors.
Figures
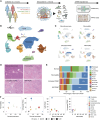
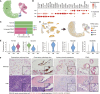
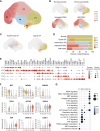
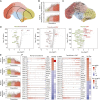



References
-
- de Visser KE, Joyce JA. The evolving tumor microenvironment: from cancer initiation to metastatic outgrowth. Cancer Cell 2023;41:374–403. - PubMed
-
- Orimo A, Gupta PB, Sgroi DC, Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Delaunay T, Naeem R, et al. . Stromal fibroblasts present in invasive human breast carcinomas promote tumor growth and angiogenesis through elevated SDF-1/CXCL12 secretion. Cell 2005;121:335–48. - PubMed
-
- Kraman M, Bambrough PJ, Arnold JN, Roberts EW, Magiera L, Jones JO, et al. . Suppression of antitumor immunity by stromal cells expressing fibroblast activation protein-alpha. Science 2010;330:827–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

