Pesticide Exposure and Its Association with Parkinson's Disease: A Case-Control Analysis
- PMID: 39485576
- PMCID: PMC11530492
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-024-01501-5
Pesticide Exposure and Its Association with Parkinson's Disease: A Case-Control Analysis
Abstract
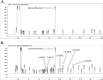
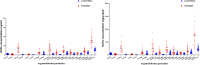
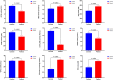
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a complex disorder that arises from genetic and environmental factors. The current investigation endeavors to investigate the role of exposure to organochlorine (OCPs) and organophosphate pesticides (OPPs), recognized as the main environmental elements, in the genesis of PD. In this case-control study, 29 PD patients and 51 healthy subjects were involved. Gas chromatography was performed to measure the serum levels of organochlorine chemicals (2,4-DDT, 4,4-DDT, 2,4-DDE, 4,4-DDE, α-HCH, β-HCH, and γ-HCH). Furthermore, acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity, arylesterase activity of paraoxonase-1 (PON-1), and several oxidative stress (OS) markers were assessed. The levels of OCPs in the PD patients were significantly higher than in the control subjects. In addition, AChE activity, arylesterase activity of PON-1, catalase activity, and superoxide dismutase 3 activity in PD patients were significantly less than controls. However, the levels of carbonyl protein, total antioxidant capacity, malondialdehyde, and nitric oxide in PD patients were higher than the controls. The findings of this investigation have indicated that OCPs and OPPs exposure could contribute to the development of Parkinson's disease. This potential linkage could either be established through the direct impact of these pesticides on the nervous system, leading to neurotoxicity, or via an indirect route through the triggering of OS.
Keywords: Organochlorine pesticides; Organophosphate pesticides; Oxidative stress; Parkinson’s disease; Pesticide exposure.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Abdollahdokht D, Asadikaram G, Abolhassani M, Pourghadamyari H, Abbasi-Jorjandi M, Faramarz S, Nematollahi MH (2021) Pesticide exposure and related health problems among farmworkers’ children: a case-control study in southeast Iran. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(40):57216–57231. 10.1007/s11356-021-14319-1 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arabuli L, Lovecka P, Jezek R, Viktorova J, Macek T, Junkova P, Gakhokidze R, Sharifianjazi F, Esmaeilkhanian A, Salahshour P (2023) AChE inhibitory effect, anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of cyclen and L-Dopa related compounds: targeting in neurodegenerative disease. J Mol Struct 1287:135665. 10.1016/j.molstruc.2023.135665 - DOI
-
- Baik D, Yu YM, Jung S-Y, Kang H-Y (2022) Prevalence and patterns of the concurrent use of anticholinergics for the motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease and acetylcholinesterase inhibitors in Parkinson’s disease patients with dementia: a cross-sectional study using Korea National Health Insurance claims data. BMC Geriatr 22(1):1–10. 10.1186/s12877-022-03296-w - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barmaki H, Morovati A, Eydivandi Z, Naleshkenani FJ, Saedi S, Musavi H, Abbasi M, Hemmati-Dinarvand M (2021) The association between serum oxidative stress indexes and pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease in the northwest of Iran. Iran J Public Health 50(3):606. 10.18502/ijph.v50i3.5621 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

