Regression analysis of topological indices for predicting efficacy of Alzheimer's drugs
- PMID: 39485746
- PMCID: PMC11530053
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0309477
Regression analysis of topological indices for predicting efficacy of Alzheimer's drugs
Abstract
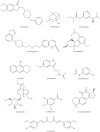
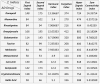
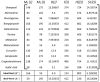
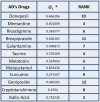
Alzheimer's Disease(AD) is the most common type of dementia. It is a progressive disease beginning with mild memory loss and possibly leading to loss of the ability to carry on a conversation and respond to the environment. This study investigates the relationship between the chemical structure of potential AD drugs and their therapeutic efficacy using Multi-Criteria Decision-Making (MCDM) techniques including The approach for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS) and Simple Additive Weighting (SAW) method. A comprehensive dataset comprising molecular descriptors and corresponding pharmacological properties, i.e., melting point, boiling point, molecular weight and density of AD drugs was compiled from diverse sources. Topological indices were calculated to capture the structural characteristics of these compounds. Application of TOPSIS and SAW through Entropy method helps obtain optimal drugs for curing AD. Quantitative Structure Property Relationships (QSPR) analysis has been done between properties and topological indices of AD's drug structures. Results revealed significant relations between specific topological indices and drug efficacy, providing insights into the structural features crucial for AD treatment efficacy. This approach offers a promising avenue for rational drug design and optimization in the quest for novel AD therapeutics.
Copyright: © 2024 Ashraf et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures









References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association. (2022). Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s and Dementia, 18(1), e1–e98. - PubMed
-
- Todeschini, R., Consonni, V. (2000). Handbook of molecular descriptors. Wiley-VCH.
-
- Roy K., Mitra I., and Kar S. (2015). Topological descriptors in drug discovery and development. Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology, 118(1-2), 22–43.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

