The significance of miR-124 in the diagnosis and prognosis of glioma: A systematic review
- PMID: 39485747
- PMCID: PMC11530070
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312250
The significance of miR-124 in the diagnosis and prognosis of glioma: A systematic review
Abstract
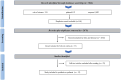
Glioma is a type of cancer that affects the central nervous system and necessitates a non-invasive diagnostic and prognostic assessment. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play a crucial role in glioma and can provide valuable information about the prognosis of patients with this condition. MiR-124 is associated with molecules that play crucial roles in cellular processes, and any disruption in its expression can have a detrimental effect on cells, potentially leading to cancer. Therefore, miR-124 can be a valuable biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis in glioma. This review aims to highlight the role of miR-124 as a diagnostic and prognostic factor in glioma. To address this issue, we systemically reviewed and used various search strategies across three databases (PubMed, Web of Science and Scopus) and then yielded 3046 records from inception to September 2023. Records that did not meet our inclusion criteria were excluded. Following the screening process, our analysis included and summarized 13 eligible studies that not only measured miR-124 in serum, plasma, and tissue of glioma patients but also provided insights intomiR-124 as a prognostic and diagnostic biomarker. Thirteen studies were included for diagnostic accuracy, and five were considered for prognostic importance of miR-124. Based on our results, a single study showed an increase in miR-124 levels in exosomes obtained from patient serum, whereas the data from the 12 studies analyzed consistently pointed towards a reduction in miR-124 levels in various glioma samples. In conclusion, our findings suggest that miR-124 may be a useful diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in glioma. However, further investigations are required to draw more definitive conclusions.
Copyright: © 2024 Ghasemi et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical