A dual role for PSIP1/LEDGF in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 39485844
- PMCID: PMC11529709
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ado6765
A dual role for PSIP1/LEDGF in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
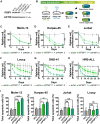
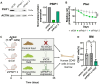
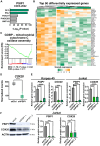
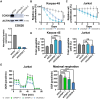
T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) is an aggressive hematological malignancy. Current intensified therapeutic protocols coincide with severe side effects, and no salvage therapy is available for primary therapy-resistant or relapsed patients. This highlights the need to identify new therapeutic targets in T-ALL. PSIP1, dispensable for normal hematopoiesis, is a dependency factor in KMT2A-rearranged myeloid leukemia. Nonetheless, loss-of-function mutations suggest a tumor suppressor role for PSIP1 in T-ALL. Here, we demonstrate that the loss of Psip1 accelerates T-ALL initiation in mice which we correlated with reduced H3K27me3 binding. Contrastingly, loss of PSIP1 impaired cell proliferation in several T-ALL cell lines. In cell lines, PSIP1 down-regulation leads to a reduction of COX20, an assembly factor of the cytochrome c oxidase in the mitochondria, and to a reduction in mitochondrial respiration. This indicates that PSIP1 can exert a dual role in the context of T-ALL, either as a tumor suppressor gene during tumor initiation or as a dependency factor in tumor maintenance.
Figures



References
-
- Hunger S. P., Mullighan C. G., Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children. N. Engl. J. Med. 373, 1541–1552 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Marks D. I., Rowntree C., Management of adults with T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 129, 1134–1142 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Eidahl J. O., Crowe B. L., North J. A., McKee C. J., Shkriabai N., Feng L., Plumb M., Graham R. L., Gorelick R. J., Hess S., Poirier M. G., Foster M. P., Kvaratskhelia M., Structural basis for high-affinity binding of LEDGF PWWP to mononucleosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 41, 3924–3936 (2013). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

