Mouse α-synuclein fibrils are structurally and functionally distinct from human fibrils associated with Lewy body diseases
- PMID: 39485845
- PMCID: PMC11800946
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adq3539
Mouse α-synuclein fibrils are structurally and functionally distinct from human fibrils associated with Lewy body diseases
Abstract
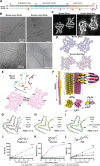
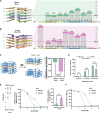
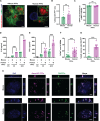
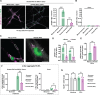
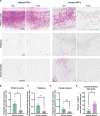
The intricate process of α-synuclein aggregation and fibrillization holds pivotal roles in Parkinson's disease (PD) and multiple system atrophy (MSA). While mouse α-synuclein can fibrillize in vitro, whether these fibrils commonly used in research to induce this process or form can reproduce structures in the human brain remains unknown. Here, we report the first atomic structure of mouse α-synuclein fibrils, which was solved in parallel by two independent teams. The structure shows striking similarity to MSA-amplified and PD-associated E46K fibrils. However, mouse α-synuclein fibrils display altered packing arrangements, reduced hydrophobicity, and heightened fragmentation sensitivity and evoke only weak immunological responses. Furthermore, mouse α-synuclein fibrils exhibit exacerbated pathological spread in neurons and humanized α-synuclein mice. These findings provide critical insights into the structural underpinnings of α-synuclein pathogenicity and emphasize a need to reassess the role of mouse α-synuclein fibrils in the development of related diagnostic probes and therapeutic interventions.
Figures


References
-
- Pollanen M. S., Dickson D. W., Bergeron C., Pathology and biology of the Lewy body. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 52, 183–191 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Spillantini M. G., Schmidt M. L., Lee V. M., Trojanowski J. Q., Jakes R., Goedert M., α-Synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388, 839–840 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Schweighauser M., Shi Y., Tarutani A., Kametani F., Murzin A. G., Ghetti B., Matsubara T., Tomita T., Ando T., Hasegawa K., Murayama S., Yoshida M., Hasegawa M., Scheres S. H. W., Goedert M., Structures of α-synuclein filaments from multiple system atrophy. Nature 585, 464–469 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yang Y., Shi Y., Schweighauser M., Zhang X., Kotecha A., Murzin A. G., Garringer H. J., Cullinane P. W., Saito Y., Foroud T., Warner T. T., Hasegawa K., Vidal R., Murayama S., Revesz T., Ghetti B., Hasegawa M., Lashley T., Scheres S. H. W., Goedert M., Structures of α-synuclein filaments from human brains with Lewy pathology. Nature 610, 791–795 (2022). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yang Y., Garringer H. J., Shi Y., Lövestam S., Peak-Chew S., Zhang X., Kotecha A., Bacioglu M., Koto A., Takao M., Spillantini M. G., Ghetti B., Vidal R., Murzin A. G., Scheres S. H. W., Goedert M., New SNCA mutation and structures of α-synuclein filaments from juvenile-onset synucleinopathy. Acta Neuropathol. 145, 561–572 (2023). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

