Clinical effect and contributing factors of acupuncture for knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and pairwise and exploratory network meta-analysis
- PMID: 39486882
- PMCID: PMC11672105
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjebm-2023-112626
Clinical effect and contributing factors of acupuncture for knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and pairwise and exploratory network meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: This study aims to evaluate (1) the effect and safety of acupuncture in patients with knee osteoarthritis (KOA) and explore (2) whether the effect of acupuncture differed according to acupuncture type, acupuncture dose and follow-up time.
Design: Systematic review and pairwise and exploratory network meta-analysis.
Setting: PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, Web of Science, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, Chinese Biomedical Literature Database, VIP Database for Chinese Technical Periodicals and Wanfang from inception to 13 November 2023.
Participants: Randomised controlled trials comparing acupuncture with sham acupuncture, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), usual care or waiting list groups, intra-articular (IA) injection and blank groups in patients with KOA.
Interventions: Eligible interventions included manual acupuncture (MA) and electroacupuncture (EA).
Main outcomes measures: The primary outcome was pain intensity at the end of treatment.
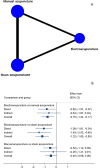
Results: 80 trials (9933 participants) were included. Very low certainty evidence suggested that acupuncture may reduce pain intensity compared with sham acupuncture (standardised mean difference, SMD -0.74, 95% CI -1.08 to -0.39, corresponded to a difference in Visual Analogue Scale of -18.50 mm, -27.00 to -9.75), NSAIDs (SMD -0.86 -1.26 to -0.46, corresponded to -21.50 mm, -31.50 to -11.50), usual care or waiting list groups (SMD -1.01, -1.47 to -0.54, corresponded to -25.25 mm, -36.75 to -13.50) and blank groups (SMD -1.65, -1.99 to -1.32, corresponded to -41.25 mm, -49.75 to -33.00), but not IA injection. Similar results were also found in other outcomes. For most of the subgroup analyses, acupuncture type, acupuncture dose and follow-up time did not show a significant relative effect. Only when compared with NSAIDs, a higher dose of acupuncture may provide greater pain relief (interaction p<0.001). The network meta-analysis revealed that electroacupuncture (SMD -0.75, 95% CI -1.34 to -0.17) had a greater effect on pain relief in patients with KOA compared with manual acupuncture.
Conclusions: The findings suggest that acupuncture may provide clinically important effects in reducing pain and improving physical function in patients with KOA, but the certainty of evidence was very low. Electroacupuncture and higher dose of acupuncture probably are two potential contributing factors.
Prospero registration number: CRD42021232177.
Keywords: Acupuncture; Knee; PAIN MANAGEMENT.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


References
-
- GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. 2016;388:1545–602. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
