Human iPSC-derived neural stem cells displaying radial glia signature exhibit long-term safety in mice
- PMID: 39487141
- PMCID: PMC11530573
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-53613-7
Human iPSC-derived neural stem cells displaying radial glia signature exhibit long-term safety in mice
Abstract
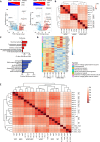
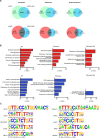
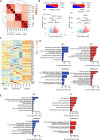
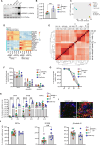
Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural stem/progenitor cells (hiPSC-NSCs) hold promise for treating neurodegenerative and demyelinating disorders. However, comprehensive studies on their identity and safety remain limited. In this study, we demonstrate that hiPSC-NSCs adopt a radial glia-associated signature, sharing key epigenetic and transcriptional characteristics with human fetal neural stem cells (hfNSCs) while exhibiting divergent profiles from glioblastoma stem cells. Long-term transplantation studies in mice showed robust and stable engraftment of hiPSC-NSCs, with predominant differentiation into glial cells and no evidence of tumor formation. Additionally, we identified the Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Transcription Factor 1 (SREBF1) as a regulator of astroglial differentiation in hiPSC-NSCs. These findings provide valuable transcriptional and epigenetic reference datasets to prospectively define the maturation stage of NSCs derived from different hiPSC sources and demonstrate the long-term safety of hiPSC-NSCs, reinforcing their potential as a viable alternative to hfNSCs for clinical applications.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Gage, F. H. & Temple, S. Neural stem cells: generating and regenerating the brain. Neuron80, 588–601 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Trounson, A. & McDonald, C. Stem cell therapies in clinical trials: progress and challenges. Cell Stem Cell17, 11–22 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Lu, P., Jones, L. L., Snyder, E. Y. & Tuszynski, M. H. Neural stem cells constitutively secrete neurotrophic factors and promote extensive host axonal growth after spinal cord injury. Exp. Neurol.181, 115–129 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

