Narrative predicts cardiac synchrony in audiences
- PMID: 39487185
- PMCID: PMC11530447
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-73066-8
Narrative predicts cardiac synchrony in audiences
Abstract
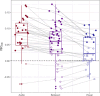
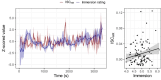
Audio-visual media possesses a remarkable ability to synchronise audiences' neural, behavioural, and physiological responses. This synchronisation is considered to reflect some dimension of collective attention or engagement with the stimulus. But what is it about these stimuli that drives such strong engagement? There are several properties of media stimuli which may lead to synchronous audience response: from low-level audio-visual features, to the story itself. Here, we present a study which separates low-level features from narrative by presenting participants with the same content but in separate modalities. In this way, the presentations shared no low-level features, but participants experienced the same narrative. We show that synchrony in participants' heart rate can be driven by the narrative information alone. We computed both visual and auditory perceptual saliency for the content and found that narrative was approximately 10 times as predictive of heart rate as low-level saliency, but that low-level audio-visual saliency has a small additive effect towards heart rate. Further, heart rate synchrony was related to a separate cohorts' continuous ratings of immersion, and that synchrony is likely to be higher at moments of increased narrative importance. Our findings demonstrate that high-level narrative dominates in the alignment of physiology across viewers.
Keywords: Audiences; Immersion; Narrative; Physiological synchrony; Story.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Statista Average daily media use in the United States in 3rd quarter of 2022, by medium (in hours.minutes). https://www.statista.com/statistics/1289938/daily-media-usage-us/
-
- Green, M. C. & Brock, T. C. The role of transportation in the persuasiveness of public narratives. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol.79, 701–721 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Busselle, R. W. & Bilandzic, H. Measuring Narrative Engagement. Media Psychol.12, 321–347 (2009).
-
- Csikszentmihalyi, M. & Flow The Psychology of Optimal Experience. in (Harper & Row, (1990).
-
- Agrawal, S., Simon, A., Bech, S., Bærentsen, K. & Forchhammer, S. Defining immersion: Literature Review and implications for Research on Audiovisual experiences. J. Audio Eng. Soc.68, 404–417 (2020).
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

