A novel stability-indicating chromatographic quantification of the antiparkinsonian drug safinamide in its pharmaceutical formulation employing HPTLC densitometry and ion-pair HPLC-DAD
- PMID: 39487557
- PMCID: PMC11529230
- DOI: 10.1186/s13065-024-01315-y
A novel stability-indicating chromatographic quantification of the antiparkinsonian drug safinamide in its pharmaceutical formulation employing HPTLC densitometry and ion-pair HPLC-DAD
Abstract
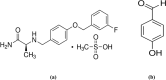
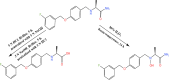
Parkinson's disease (PD) emerges as a notable health concern among the elderly population. Safinamide mesylate (SAF) is a novel and emerging add-on therapy in PD treatment. The stability of innovative drug formulations and the development of appropriate stability-indicating methods are of great importance to modern pharmaceutical analysis. The current work has established novel comprehensive stability-indicating chromatographic approaches, HPTLC coupled with densitometric quantification and HPLC-DAD, for the selective assay of SAF in pharmaceutical formulation along with its synthetic precursor impurity; 4-hydroxy benzaldehyde (4-HBD) in presence of its stress induced degradation products. The stability of SAF was investigated under different stress conditions. It was found that SAF is likely to undergo acid, base hydrolysis, and oxidative degradation. Using mass spectrometry and infrared spectroscopy, the structures of the forced degradation products were confirmed and elucidated. The dissolution behavior of Parkimedine® Tablets was also monitored in the FDA suitable medium. Multiple assessment tools were used to evaluate the environmental sustainability of the proposed methods and the reported one. The greenness tools included Complex-GAPI and AGREE metrics. In addition, the innovative concepts of "blueness" and "whiteness" evaluation were incorporated through the newly introduced BAGI and RGB12 algorithms, respectively.
Keywords: 4-hydroxy benzaldehyde; Blueness assessment; Greenness assessment; HPLC–DAD; HPTLC-densitometry; In-vitro release; RGB12 model; Safinamide Mesylate; Stability indicating methods.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Nutt JG. Motor fluctuations and dyskinesia in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2001;8:101–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
