Assessment of Urolithin A effects on muscle endurance, strength, inflammation, oxidative stress, and protein metabolism in male athletes with resistance training: an 8-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study
- PMID: 39487653
- PMCID: PMC11536656
- DOI: 10.1080/15502783.2024.2419388
Assessment of Urolithin A effects on muscle endurance, strength, inflammation, oxidative stress, and protein metabolism in male athletes with resistance training: an 8-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to investigate the impact of Urolithin A (UA) on muscle endurance, muscle strength, inflammatory levels, oxidative stress, and protein metabolism status in resistance-trained male athletes.
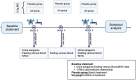
Method: An 8-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study was conducted with twenty resistance-trained male athletes. Participants were supplemented with 1 g of UA daily. Muscle strength and muscle endurance measures were assessed, and fasting venous blood samples and morning urine samples were collected to evaluate their oxidative stress levels, inflammatory markers, and protein metabolism status.
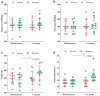
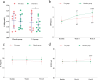
Results: There were no significant differences observed in terms of dietary energy intake and composition between the two assessments conducted within a 24-hour period. After 8 weeks of UA supplementation, compared to baseline measurements, the UA group exhibited increases in 1RM bench press and squat, although these changes were not statistically significant (Δ = 3.00 ± 0.17 kg, p = 0.051, Δ = 1.35 ± 2.73 kg, p = 0.499). However, significant improvements were noted in Maximum Voluntary Isometric Contraction (MVIC) and repetitions to failure (RTF) performance (Δ = 36.10 ± 0.62 NM, p = 0.000; Δ = 2.00 ± 0.56, p = 0.001). When compared to the placebo group, the UA supplementation for 8 weeks led to an increase in 1RM bench press and squat, although statistical significance was not reached (Δ = 3.50 ± 0.79 kg, p = 0.462; Δ = 2.55 ± 1.36 kg, p = 0.710). Furthermore, the group receiving UA supplementation, compared to the placebo group, showed significant improvements in MVIC and RTF (Δ = 43.50 ± 0.77 NM, p = 0.048; Δ = 2.00 ± 1.22, p = 0.011), indicating that the UA group exhibited superior performance enhancements in these metrics compared to the placebo group. After 8 weeks of UA supplementation, the UA group showed a significant decrease in 3-methylhistidine (3-MH) compared to baseline measurement (Δ=-2.38 ± 1.96 μmol/L, p = 0.049). Additionally, the UA group exhibited a significant increase in C-reactive protein (CRP) compared to baseline (Δ = 0.71 ± 0.21 mg/L, p = 0.001). However, there was no significant changes observed in Interleukin-6 (IL-6) (Δ=-1.00 ± 1.01 pg/mL, p = 0.076), or superoxide dismutase (SOD) (Δ=-0.004 ± 0.72 U/mL, p = 0.996) compared to baseline in the UA group. When compared to the placebo group, there was no significant difference observed in 3-MH in the UA group (Δ=-3.20 ± 0.31 μmol/L, p = 0.36). In terms of inflammation markers, the UA group exhibited a significant decrease in CRP (Δ=-0.79 ± 0.38 mg/L, p = 0.032) compared to the placebo group, whereas there was a decrease in IL-6 without statistical significance (Δ=-1.75 ± 0.45 pg/mL, p = 0.215). Furthermore, the UA group showed a significant decrease in SOD compared to the placebo group (Δ=-4.32 ± 0.90 U/mL, p = 0.041).
Conclusions: After 8 weeks of UA supplementation at 1 g/day, resistance-trained male athletes showed improvements in muscle strength and endurance. Additionally, UA supplementation was also associated with reduced oxidative stress levels and a decrease in inflammation response levels.
Keywords: Urolithin A; ergogenic aid; exercise performance; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
