Prostaglandin E Receptor 2 (EP2) Dysregulation in Allergic Fungal Rhinosinusitis Nasal Polyp Epithelium
- PMID: 39487665
- PMCID: PMC11903372
- DOI: 10.1002/lary.31868
Prostaglandin E Receptor 2 (EP2) Dysregulation in Allergic Fungal Rhinosinusitis Nasal Polyp Epithelium
Abstract
Objectives: Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis (AFRS) is an eosinophilic subtype of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis (CRSwNP). This study aimed to investigate the transcriptome of AFRS nasal polyp epithelium.
Methods: Sinonasal epithelial cells were harvested from healthy nasal mucosa and polyp tissue collected from participants undergoing elective sinonasal surgery. Primary epithelial cells were subsequently grown in air/liquid interface and subjected to RNA-seq analysis, RT-qPCR, immunoblotting, and immunostaining.
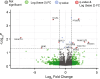
Results: A total of 19 genes were differentially expressed between healthy and AFRS sample epithelium. The second top candidate gene, ranked by adjusted p-value, was prostaglandin E receptor 2 (PTGER2). The upregulation of PTGER2 was confirmed by RT-qPCR and immunoblot. The presence of the EP2 receptor, encoded by the PTGER2 gene, was confirmed by immunocytochemistry.
Conclusion: PTGER2 is a potential novel therapeutic target for AFRS. EP2 dysregulation is associated with aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease, potentially giving insight into common mechanisms of disease in severe CRSwNP.
Level of evidence: NA Laryngoscope, 135:S1-S8, 2025.
Keywords: allergic fungal sinusitis; eicosanoid receptor; nasal polyposis; prostaglandin E receptors.
© 2024 The Author(s). The Laryngoscope published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. This article has been contributed to by U.S. Government employees and their work is in the public domain in the USA.
Figures





References
-
- Kim J, Makary CA, Roland LT, et al. What is allergic fungal sinusitis: a call to action. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2022;12:141‐146. - PubMed
-
- Campbell JM, Graham M, Gray HC, Bower C, Blaiss MS, Jones SM. Allergic fungal sinusitis in children. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2006;96:286‐290. - PubMed
-
- Ghegan MD, Wise SK, Gorham E, Schlosser RJ. Socioeconomic factors in allergic fungal rhinosinusitis with bone erosion. Am J Rhinol. 2007;21:560‐563. - PubMed
-
- Wise SK, Ghegan MD, Gorham E, Schlosser RJ. Socioeconomic factors in the diagnosis of allergic fungal rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008;138:38‐42. - PubMed
-
- Miller JD, Deal AM, McKinney KA, et al. Markers of disease severity and socioeconomic factors in allergic fungal rhinosinusitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2014;4:272‐279. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

