Charge-assisted stabilization of lipid nanoparticles enables inhaled mRNA delivery for mucosal vaccination
- PMID: 39488531
- PMCID: PMC11531489
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-53914-x
Charge-assisted stabilization of lipid nanoparticles enables inhaled mRNA delivery for mucosal vaccination
Abstract
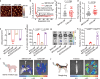
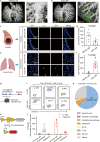
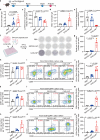
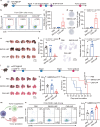
Inhaled delivery of messenger RNA (mRNA) using lipid nanoparticle (LNP) holds immense promise for treating pulmonary diseases or serving as a mucosal vaccine. However, the unsatisfactory delivery efficacy caused by the disintegration and aggregation of LNP during nebulization represents a major obstacle. To address this, we develop a charge-assisted stabilization (CAS) strategy aimed at inducing electrostatic repulsions among LNPs to enhance their colloidal stability. By optimizing the surface charges using a peptide-lipid conjugate, the leading CAS-LNP demonstrates exceptional stability during nebulization, resulting in efficient pulmonary mRNA delivery in mouse, dog, and pig. Inhaled CAS-LNP primarily transfect dendritic cells, triggering robust mucosal and systemic immune responses. We demonstrate the efficacy of inhaled CAS-LNP as a vaccine for SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant and as a cancer vaccine to inhibit lung metastasis. Our findings illustrate the design principles of nebulized LNPs, paving the way of developing inhaled mRNA vaccines and therapeutics.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
X.L. and S.L. are inventors on a patent application (No. PCT/CN2023/130743) held by the Institute of Chemistry Chinese Academy of Sciences that covers the design and applications of CAS-LNP reported in this study. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Barbier, A. J., Jiang, A. Y., Zhang, P., Wooster, R. & Anderson, D. G. The clinical progress of mRNA vaccines and immunotherapies. Nat. Biotechnol.40, 840–854 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Neutra, M. R. & Kozlowski, P. A. Mucosal vaccines: The promise and the challenge. Nat. Rev. Immunol.6, 148–158 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Shaffer, C. Mist begins to clear for lung delivery of RNA. Nat. Biotechnol.38, 1110–1112 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

