Epigenetic Activation of the CMTM6-IGF2BP1-EP300 Positive Feedback Loop Drives Gemcitabine Resistance in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 39488785
- PMCID: PMC11653652
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202406714
Epigenetic Activation of the CMTM6-IGF2BP1-EP300 Positive Feedback Loop Drives Gemcitabine Resistance in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
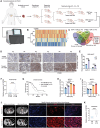
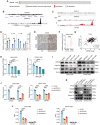
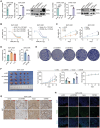
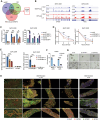
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a highly malignant tumor with a dismal prognosis. Gemcitabine-based chemotherapy has emerged as a first-line treatment for PDAC. However, the development of gemcitabine resistance often results in therapeutic failure. In order to uncover the underlying mechanisms of gemcitabine resistance, gemcitabine-resistant PDAC cell lines and patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models are established and subjected to RNA sequencing. It is found that CMTM6 is closely related to gemcitabine resistance in PDAC. Multi-omics analysis revealed that EP300-mediated H3K27ac modification is involved in the transcriptional activation of CMTM6, which maintains IGF2BP1 expression by preventing its ubiquitination. The m6A reader IGF2BP1 stabilizes the EP300 and MYC mRNAs by recognizing m6A modifications, forming a positive feedback loop that enhances tumor stemness and ultimately contributes to PDAC resistance. The combined application of the EP300 inhibitor inobrodib and gemcitabine exerts a synergistic effect on PDAC. Overall, these findings reveal that the EP300-CMTM6-IGF2BP1 positive feedback loop facilitates gemcitabine resistance via epigenetic reprogramming and the combined use of inobrodib and gemcitabine represents a promising strategy for overcoming chemoresistance in PDAC, warranting further investigation in clinical trials.
Keywords: CMTM6; N6‐methyladenosine; chemoresistance; epigenetic modification; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Collaborators G. B. D. P. C., Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 934.
-
- Oettle H., Neuhaus P., Hochhaus A., Hartmann J. T., Gellert K., Ridwelski K., Niedergethmann M., Zulke C., Fahlke J., Arning M. B., Sinn M., Hinke A., Riess H., JAMA, J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2013, 310, 1473. - PubMed
-
- Han W., Ding P., Xu M., Wang L., Rui M., Shi S., Liu Y., Zheng Y., Chen Y., Yang T., Ma D., Genomics 2003, 81, 609. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82072644/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82203473/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82203105/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82103401/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 202201010927/Guangzhou Science and Technology Program Project
- 2022A1515111221/Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Province
- 2021A1515111104/Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Province
- 2021A1515010123/Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Province
- 2023A1515110874/Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Province
- 2024A1515010487/Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
