Endosomal Trafficking Bypassed by the RAB5B-CD109 Interplay Promotes Axonogenesis in KRAS-Mutant Pancreatic Cancer
- PMID: 39488792
- PMCID: PMC11653710
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202405092
Endosomal Trafficking Bypassed by the RAB5B-CD109 Interplay Promotes Axonogenesis in KRAS-Mutant Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
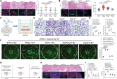
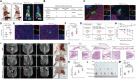
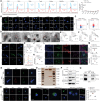
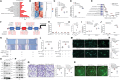
Perineural invasion (PNI) represents a unique biological feature associated with poor prognosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), especially in the presence of KRAS mutations. Extracellular vesicle (EV)-packaged circular RNAs (circRNAs) function as essential mediators of tumor microenvironment communication, triggering PDAC cell invasion and distant metastasis. However, the regulatory mechanisms of EV-packaged circRNAs in the PNI of KRAS-mutant PDAC have not yet been elucidated. Herein, a KRASG12D mutation-responsive EV-packaged circRNA, circPNIT, which positively correlated with PNI in PDAC patients is identified. Functionally, KRASG12D PDAC-derived EV-packaged circPNIT promoted axonogenesis and PNI both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, the circPNIT-mediated Rab5B-CD109 interplay bypassed traditional endosomal trafficking to anchor Rab5B to the lipid rafts of multivesicular bodies and packaged circPNIT into CD109+ EVs. Subsequently, CD109+ EVs delivered circPNIT to neurons by binding to TRPV1 and facilitating DSCAML1 transcription-induced axonogenesis, which in turn enhanced the PNI by activating the GFRα1/RET pathway. Importantly, circPNIT-loaded CD109+ EVs are established to dramatically promote PNI in a KRASG12D/+ Trp53R172H/+ Pdx-1-Cre mouse model. Collectively, the findings highlight the mechanism underlying how EV-packaged circRNAs mediate the PNI of KRAS-mutant PDAC cells through the Rab5B endosomal bypass, identifying circPNIT as an effective target for the treatment of neuro-metastatic PDAC.
Keywords: KRAS mutation; circular RNA; engineered extracellular vesicle; pancreatic cancer; perineural invasion.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Siegel R. L., Miller K. D., Wagle N. S., Jemal A., CA Cancer J Clin 2023, 73, 17. - PubMed
-
- a) Lemstrova R., Brynychova V., Hughes D. J., Hlavac V., Dvorak P., Doherty J. E., Murray H. A., Crockard M., Oliverius M., Hlavsa J., Honsova E., Mazanec J., Kala Z., Lovecek M., Havlik R., Ehrmann J., Strouhal O., Soucek P., Melichar B., Mohelnikova‐Duchonova B., Oncol Lett 2017, 14, 5980; - PMC - PubMed
- b) Nakao A., Harada A., Nonami T., Kaneko T., Takagi H., Pancreas 1996, 12, 357; - PubMed
- c) Amit M., Na'ara S., Gil Z., Nature reviews. Cancer 2016, 16, 399. - PubMed
-
- a) Chang W.‐H., Nguyen T.‐T. T., Hsu C.‐H., Bryant K. L., Kim H. J., Ying H., Erickson J. W., Der C. J., Cerione R. A., Antonyak M. A., Cancer Lett 2021, 517, 66; - PMC - PubMed
- b) Luo Y., Li Z., Kong Y., He W., Zheng H., An M., Lin Y., Zhang D., Yang J., Zhao Y., Chen C., Chen R., J. Clin. Invest. 2022, 132, 157644. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2022YFA1305500/Key Technologies Research and Development Program
- 2018YFA0902803/Key Technologies Research and Development Program
- 82072639/National Science Foundation
- 82173272/National Science Foundation
- 82103536/National Science Foundation
- 82202276/National Science Foundation
- 82103416/National Science Foundation
- 82203691/National Science Foundation
- 2023A1515011648/Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation
- 2021B1515020091/Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation
- 2022A1515012288/Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation
- 2021A1515010355/Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
