Paradoxical brain herniation following decompressive craniectomy: A case series and systematic review of literature
- PMID: 39489102
- PMCID: PMC11567043
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2024.110477
Paradoxical brain herniation following decompressive craniectomy: A case series and systematic review of literature
Abstract
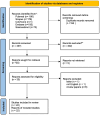
Introduction: Paradoxical brain herniation (PBH) represents a rare and potentially life-threatening complication observed in individuals following decompressive craniectomy. Its diagnosis necessitates a high level of suspicion, combined with clinical and imaging evidence, such as midline shift, herniation, and a decreased Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS). Given the rarity and severity of this condition, we conduct a comprehensive literature review to identify all documented predisposing factors, clinical presentations, and appropriate clinical management. This review will serve as a guide for effective treatment strategies.
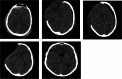
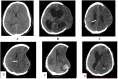
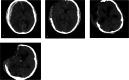
Case presentation: In this report, we document three cases of post-traumatic PBH following decompressive craniectomy. The patient's predisposing factor was a lumbar puncture, with two cases resolving after Terendlenburg repositioning, hydration, and elective cranioplasty. The third case developed PBH after external ventricular drainage (EVD) insertion. Although the patient's GCS improved after clamping the EVD and hydration, the patient ultimately succumbed to meningitis.
Clinical discussion: The primary clinical manifestations of PBH often encompass a diminished GCS alongside radiographic evidence of midline shift and brain herniation. Various precipitating factors have been associated with PBH after decompressive craniectomy, including CSF drainage, dehydration, and upright positioning, although instances of spontaneous PBH have been documented. Reported therapeutic strategies encompass rehydration, Trendelenburg positioning, temporary cessation of CSF drainage, and cranioplasty.
Conclusion: Given the infrequency of PBH and the potential for misdiagnosis with brain edema, it is imperative to consider this condition in every patient who experiences a decreased level of consciousness following decompressive craniectomy.
Keywords: Cranioplasty; Decompressive craniectomy; Paradoxical brain herniation; Trendelenburg.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest All authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Paradoxical Brain Herniation After Decompressive Craniectomy Provoked by Drainage of Subdural Hygroma.World Neurosurg. 2016 Jul;91:673.e1-4. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2016.04.041. Epub 2016 Apr 20. World Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 27108031
-
Paradoxical transtentorial herniation caused by lumbar puncture after decompressive craniectomy.J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2012 Feb;51(2):102-4. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2012.51.2.102. Epub 2012 Feb 29. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2012. PMID: 22500203 Free PMC article.
-
Lumbar puncture as possible cause of sudden paradoxical herniation in patient with previous decompressive craniectomy: report of two cases.BMC Neurol. 2017 Aug 2;17(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s12883-017-0931-1. BMC Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28768486 Free PMC article.
-
Complications of decompressive craniectomy for traumatic brain injury.Neurosurg Focus. 2009 Jun;26(6):E7. doi: 10.3171/2009.4.FOCUS0965. Neurosurg Focus. 2009. PMID: 19485720 Review.
-
Timing of Decompressive Craniectomy for Ischemic Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injury: A Review.Front Neurol. 2019 Jan 25;10:11. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00011. eCollection 2019. Front Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30740085 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hanko M., Snopko P., Opsenak R., Benco M., Richterova R., Kolarovszki B. Sinking skin flap syndrome and paradoxical herniation provoked by a malfunction of external lumbar drainage and CSF leak. Acta Medica Martiniana. 2019;19(3):103–110.
-
- Stiver S.I. Complications of decompressive craniectomy for traumatic brain injury. Neurosurg. Focus. 2009;26(6):E7. - PubMed
-
- Fields J.D., Lansberg M.G., Skirboll S.L., Kurien P.A., Wijman C.A. “paradoxical” transtentorial herniation due to CSF drainage in the presence of a hemicraniectomy. Neurology. 2006;67(8):1513–1514. - PubMed
-
- Oyelese AA, Steinberg GK, Huhn SL, Wijman CA. Paradoxical cerebral herniation secondary to lumbar puncture after decompressive craniectomy for a large space-occupying hemispheric stroke: case report. Neurosurgery. 2005;57(3):E594; discussion E. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

