Multicenter validation of an RNA-based assay to predict anti-PD-1 disease control in patients with recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: the PREDAPT study
- PMID: 39489541
- PMCID: PMC11535711
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2024-009573
Multicenter validation of an RNA-based assay to predict anti-PD-1 disease control in patients with recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: the PREDAPT study
Abstract
Background: Despite advances in cancer care and detection, >65% of patients with squamous cell cancer of the head and neck (HNSCC) will develop recurrent and/or metastatic disease. The prognosis for these patients is poor with a 5-year overall survival of 39%. Recent treatment advances in immunotherapy, including immune checkpoint inhibitors like pembrolizumab and nivolumab, have resulted in clinical benefit in a subset of patients. There is a critical clinical need to identify patients who benefit from these antiprogrammed cell death protein 1 (anti-PD-1) immune checkpoint inhibitors.
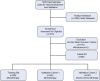
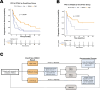
Methods: Here, we report findings from a multicenter observational study, PREDicting immunotherapy efficacy from Analysis of Pre-treatment Tumor biopsies (PREDAPT), conducted across 17 US healthcare systems. PREDAPT aimed to validate OncoPrism-HNSCC, a clinical biomarker assay predictive of disease control in patients with recurrent or metastatic HNSCC treated with anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitors as a single agent (monotherapy) and in combination with chemotherapy (chemo-immunotherapy). The test used RNA-sequencing data and machine learning models to score each patient and place them into groups of low, medium, or high.
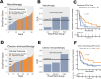
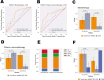
Results: The OncoPrism-HNSCC prediction significantly correlated with disease control in both the monotherapy cohort (n=62, p=0.004) and the chemo-immunotherapy cohort (n=50, p=0.01). OncoPrism-HNSCC also significantly predicted progression-free survival in both cohorts (p=0.015 and p=0.037, respectively). OncoPrism-HNSCC had more than threefold higher specificity than programmed death-ligand 1 combined positive score and nearly fourfold higher sensitivity than tumor mutational burden for predicting disease control.
Conclusions: Here, we demonstrate the clinical validity of the OncoPrism-HNSCC assay in identifying patients with disease control in response to anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Trial registration number: NCT04510129.
Keywords: biomarker; head and neck cancer; immune checkpoint inhibitor; next generation sequencing (NGS); tumor mutation burden (TMB).
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: KCF, JE, JH, RLW, MMP, DNM, JIG, and EJD are employed, have stock interests, and/or a financial relationship with Cofactor Genomics, maker of the OncoPrism-HNSCC test.
Figures
References
-
- Burtness B, Harrington KJ, Greil R, et al. Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy versus cetuximab with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-048): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. The Lancet. 2019;394:1915–28. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32591-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Larkins E, Blumenthal GM, Yuan W, et al. FDA Approval Summary: Pembrolizumab for the Treatment of Recurrent or Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma with Disease Progression on or After Platinum-Containing Chemotherapy. Oncologist. 2017;22:873–8. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2016-0496. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
