Dental pulp mesenchymal stem cell (DPSCs)-derived soluble factors, produced under hypoxic conditions, support angiogenesis via endothelial cell activation and generation of M2-like macrophages
- PMID: 39491013
- PMCID: PMC11533415
- DOI: 10.1186/s12929-024-01087-6
Dental pulp mesenchymal stem cell (DPSCs)-derived soluble factors, produced under hypoxic conditions, support angiogenesis via endothelial cell activation and generation of M2-like macrophages
Abstract
Background: Cell therapy has emerged as a revolutionary tool to repair damaged tissues by restoration of an adequate vasculature. Dental Pulp stem cells (DPSC), due to their easy biological access, ex vivo properties, and ability to support angiogenesis have been largely explored in regenerative medicine.
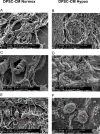
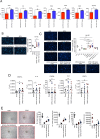
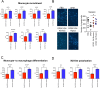
Methods: Here, we tested the capability of Dental Pulp Stem Cell-Conditioned medium (DPSC-CM), produced in normoxic (DPSC-CM Normox) or hypoxic (DPSC-CM Hypox) conditions, to support angiogenesis via their soluble factors. CMs were characterized by a secretome protein array, then used for in vivo and in vitro experiments. In in vivo experiments, DPSC-CMs were associated to an Ultimatrix sponge and injected in nude mice. After excision, Ultimatrix were assayed by immunohistochemistry, electron microscopy and flow cytometry, to evaluate the presence of endothelial, stromal, and immune cells. For in vitro procedures, DPSC-CMs were used on human umbilical-vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), to test their effects on cell adhesion, migration, tube formation, and on their capability to recruit human CD14+ monocytes.
Results: We found that DPSC-CM Hypox exert stronger pro-angiogenic activities, compared with DPSC-CM Normox, by increasing the frequency of CD31+ endothelial cells, the number of vessels and hemoglobin content in the Ultimatrix sponges. We observed that Utimatrix sponges associated with DPSC-CM Hypox or DPSC-CM Normox shared similar capability to recruit CD45- stromal cells, CD45+ leukocytes, F4/80+ macrophages, CD80+ M1-macrophages and CD206+ M2-macropages. We also observed that DPSC-CM Hypox and DPSC-CM Normox have similar capabilities to support HUVEC adhesion, migration, induction of a pro-angiogenic gene signature and the generation of capillary-like structures, together with the ability to recruit human CD14+ monocytes.
Conclusions: Our results provide evidence that DPSCs-CM, produced under hypoxic conditions, can be proposed as a tool able to support angiogenesis via macrophage polarization, suggesting its use to overcome the issues and restrictions associated with the use of staminal cells.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Cell-free device; Dental pulp stem cells; Macrophage polarization; Mesenchymal stem cells; Secretome; Tissue engineering.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

