The NEDD4-binding protein N4BP1 degrades mRNA substrates through the coding sequence independent of nonsense-mediated decay
- PMID: 39491646
- PMCID: PMC11648238
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107954
The NEDD4-binding protein N4BP1 degrades mRNA substrates through the coding sequence independent of nonsense-mediated decay
Abstract
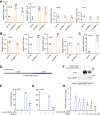
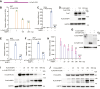
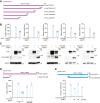
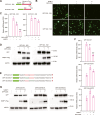
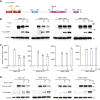
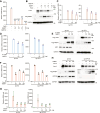
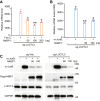
3'UTRs are recognized for their role in regulating mRNA turnover while the turnover of a specific group of mRNAs mediated by coding sequences (CDSs) remains poorly understood. N4BP1 is a critical inflammatory regulator in vivo with a molecular mechanism that is not yet clearly defined. Our study reveals that N4BP1 efficiently degrades its mRNA targets via CDS rather than the 3'-UTR. This CDS-dependent mRNA turnover mechanism appears to be a general feature of N4BP1, as evidenced by testing multiple mRNA substrates, such as Fos-C, Fos-B, Jun-B, and C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 1. Detailed mapping of the motif identified a crucial 33-nt (289-322) sequence near the 5'-end of Fos-C-CDS, where the presence of polyC is necessary for N4BP1-mediated degradation. Functional studies involving domain deletion and point mutations showed that both the K homology and N4BP1, YacP-like nuclease domains are essential for N4BP1 to restrict mRNA substrates. The function of N4BP1 in mRNA turnover is not dependent on nonsense-mediated decay as it efficiently restricts mRNA substrates even in cells deficient in UPF1, UPF3A, and UPF3B. Additionally, the function of N4BP1 is not reliant on LUC7L3 despite its known association with this protein. Our findings suggest that N4BP1 acts as an endoribonuclease to degrade mRNA substrates primarily through CDSs containing a C-rich motif.
Keywords: C-rich motif; Fos-C; KH domain; N4BP1; NYN domain; nonsense-mediated mRNA decay.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
UPF1 regulates mRNA stability by sensing poorly translated coding sequences.Cell Rep. 2024 Apr 23;43(4):114074. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114074. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38625794 Free PMC article.
-
Human UPF3A and UPF3B enable fault-tolerant activation of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay.EMBO J. 2022 May 16;41(10):e109191. doi: 10.15252/embj.2021109191. Epub 2022 Apr 22. EMBO J. 2022. PMID: 35451084 Free PMC article.
-
The Nedd4-binding partner 1 (N4BP1) protein is an inhibitor of the E3 ligase Itch.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jul 3;104(27):11280-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0701773104. Epub 2007 Jun 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17592138 Free PMC article.
-
UPFront and center in RNA decay: UPF1 in nonsense-mediated mRNA decay and beyond.RNA. 2019 Apr;25(4):407-422. doi: 10.1261/rna.070136.118. Epub 2019 Jan 17. RNA. 2019. PMID: 30655309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
No-nonsense: insights into the functional interplay of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay factors.Biochem J. 2022 May 13;479(9):973-993. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20210556. Biochem J. 2022. PMID: 35551602 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural and functional characterization of the extended-diKH domain from the antiviral endoribonuclease KHNYN.J Biol Chem. 2025 Apr;301(4):108336. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.108336. Epub 2025 Feb 19. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 39984050 Free PMC article.
-
Breaking the oncogenic link: BCL10-MALT1 disruption as a precision strike against NF-κB-driven lymphomas.Med Oncol. 2025 Jul 19;42(8):350. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02897-w. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40684038 Review.
References
-
- Hilleren P., Parker R. Mechanisms of mRNA surveillance in eukaryotes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1999;33:229–260. - PubMed
-
- Matoulkova E., Michalova E., Vojtesek B., Hrstka R. The role of the 3' untranslated region in post-transcriptional regulation of protein expression in mammalian cells. RNA Biol. 2012;9:563–576. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

