Sexual dysfunctions in inflammatory bowel disease: role of Mediterranean diet and quality of life
- PMID: 39492590
- PMCID: PMC12476212
- DOI: 10.1111/andr.13791
Sexual dysfunctions in inflammatory bowel disease: role of Mediterranean diet and quality of life
Abstract
Background: Dietary factors and chronic gastrointestinal diseases are frequent determinants of sexual dysfunctions (SD). Whether inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) are associated with SD is not well known as well as the role of diet and quality of life (QoL).
Objectives: To evaluate the prevalence of SD in a cohort of IBD patients and assess the role of clinical-demographic variables, adherence to Mediterranean diet (MD) and QoL.
Materials and methods: This is a cross-sectional observational study involving 301 patients (134 females and 167 males); 119 had Crohn's Disease and 182 had ulcerative colitis. SD were assessed through the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) and the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF). Adherence to MD was evaluated by the MD Score. QoL was investigated by the 12-item Short-Form Health Survey (SF-12) which yields summary scores of physical (PCS) and mental (MCS) health. Multiple logistic regression was used to identify predictors of SD.
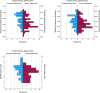
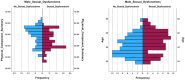
Results: Prevalence of SD in females was 61.9%, while 52.1% of males had erectile dysfunction. No differences in the prevalence of SD were found between CD and UC in both males and females. IBD activity, as defined by patient-reported outcomes, was significantly associated with SD in both sexes. In females, MD adherence score (OR 0.8, 95% CI 0.653-0.974, p = 0.027), PCS (OR = 0.936, CI 95% = 0.891-0.983, p = 0.008), and MCS (OR 0.9, 95% CI 0.906-0.985, p = 0.008) were protective against SD, whereas in males a higher PCS was associated with a lower probability of SD (OR 0.9, 95% CI 0.891-0.978, p = 0.004) DISCUSSION: IBD patients had a significant prevalence of SD which occurred more frequently in females than in males. Disease activity is associated with a higher likelihood of SD in both sexes, whereas dietary factors are differentially associated with SD in males and females. A better QoL is associated with a lower risk of SD.
Conclusion: SD is prevalent among men and women with IBD. Adherence to MD, PCS and MCS in females as well as PCS in males were protective against SD. The assessment of sexual function in IBD patients could be relevant in order to reach an early diagnosis and a timely treatment.
Keywords: FSFI; IIEF; Mediterranean diet; inflammatory bowel disease; quality of life; sexual dysfunctions.
© 2024 The Author(s). Andrology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of American Society of Andrology and European Academy of Andrology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- McCabe MP, Sharlip ID, Lewis R, et al. Incidence and prevalence of sexual dysfunction in women and men: a consensus statement from the fourth international consultation on sexual medicine 2015. J Sex Med. 2016;13:144‐152. - PubMed
-
- Laumann EO, Nicolosi A, Glasser DB, et al; GSSAB Investigators' Group . Sexual problems among women and men aged 40–80 y: prevalence and correlates identified in the global study of sexual attitudes and behaviors. Int J Impot Res. 2005;17:39‐57. - PubMed
-
- Jannini EA. SM = SM: the Interface of Systems Medicine and sexual medicine for facing non‐communicable diseases in a gender‐dependent manner. Sex Med Rev. 2017;5:349‐364. - PubMed
-
- McCabe MP, Sharlip ID, Atalla E, et al. Definitions of sexual dysfunctions in women and men: a consensus statement from the fourth international consultation on sexual medicine 2015. J Sex Med. 2016;13:135‐143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

