Novel intervention for alcohol-associated liver disease
- PMID: 39492829
- PMCID: PMC11525857
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i39.4308
Novel intervention for alcohol-associated liver disease
Abstract
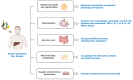
A recently published article in the World Journal of Gastroenterology clarified that elafibranor, a dual peroxisome proliferator activated receptor α/δ (PPARα/δ) agonist, reduced inflammation and fibrosis in alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD). This letter aims to discuss the findings presented in that article. ALD is a global health problem, and no effective drugs has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration to cure it. Thus, finding targeted therapies is of great urgency. Herein, we focus on the pathogenesis of ALD and the role of PPARα/δ in its development. Consistent with the conclusion of the article of interest, we think that elafibranor may be a promising therapeutic option for ALD, due to the pivotal involvement of PPARα/δ in the pathogenesis of the disease. However, its treatment dose, timing, and side effects need to be further investigated in future studies.
Keywords: Alcohol-associated liver disease; Elafibranor; Pathogenesis; Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor α/δ; Therapy.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures
References
-
- Lee BP, Witkiewitz K, Mellinger J, Anania FA, Bataller R, Cotter TG, Curtis B, Dasarathy S, DeMartini KS, Diamond I, Diazgranados N, DiMartini AF, Falk DE, Fernandez AC, German MN, Kamath PS, Kidwell KM, Leggio L, Litten R, Louvet A, Lucey MR, McCaul ME, Sanyal AJ, Singal AK, Sussman NL, Terrault NA, Thursz MR, Verna EC, Radaeva S, Nagy LE, Mitchell MC. Designing clinical trials to address alcohol use and alcohol-associated liver disease: an expert panel Consensus Statement. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bataller R, Arab JP, Shah VH. Alcohol-Associated Hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 2022;387:2436–2448. - PubMed
-
- Koizumi A, Kaji K, Nishimura N, Asada S, Matsuda T, Tanaka M, Yorioka N, Tsuji Y, Kitagawa K, Sato S, Namisaki T, Akahane T, Yoshiji H. Effects of elafibranor on liver fibrosis and gut barrier function in a mouse model of alcohol-associated liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2024;30:3428–3446. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

