Comparing the Efficacy of Renal Artery Denervation in Uncontrolled Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 39493034
- PMCID: PMC11531912
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.70805
Comparing the Efficacy of Renal Artery Denervation in Uncontrolled Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
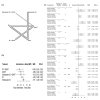
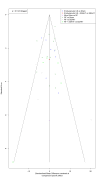
The study aims to compare the outcomes of different renal denervation (RDN) procedures in the treatment of uncontrolled hypertension. We searched Scopus, PubMed, Web of Science, and Cochrane for RCTs evaluating different procedures of RDN for hypertension. The outcomes of this study were systolic blood pressure (SBP) daytime, diastolic blood pressure (DBP) daytime, SBP nighttime, DBP nighttime, SBP 24-hour, DBP 24-hour, SBP home, DBP home, SBP office, and DBP office. We did a frequentist network meta-analysis of 38 published RCTs evaluating the efficacy of different renal artery denervation procedures for uncontrolled hypertension compared to sham procedures or standardized stepped-care antihypertensive treatment (SSAHT). Radiofrequency (RF) alone showed a statistically significant reduction in DBP (24 hours), DBP (daytime), and DBP (nighttime): standardized mean difference (SMD): -2.01 (95% CI: (-3.34; -0.68)), SMD: -4.36 (95% CI: (-8.28; -0.44)), and SMD: -3.50 (95% CI: (-6.23; -0.76)), respectively, and showed a statistically significant reduction in SBP (24 hours), SBP (daytime), and SBP (nighttime): SMD: -3.93 (95% CI: (-6.01; -1.84)), SMD: -5.88 (95% CI: (-9.91; -1.85)), and SMD: -5.79 (95% CI: (-10.0; -1.58)), respectively. RF added to SSAHT has statistical significance in the reduction of DBP (nighttime), SBP (daytime), SBP (home), and SBP (nighttime) with a SMD of -7.63 (95% CI: (-14.21; -1.06)), SMD of -10.56 (95% CI: (-21.03; -0.08)), SMD of -23.20 (95% CI: (-36.72; -9.26)), and SMD of -14.03 (95% CI: (-25.43; -2.63)), respectively. We found that renal denervation, especially by RF, when added to SSAHT may be a promising therapeutic option for patients with treatment-resistant hypertension, particularly in cases where medication alone fails to achieve adequate blood pressure control.
Keywords: hypertension; network meta-analysis; radiofrequency; renal artery; renal denervation.
Copyright © 2024, Abouelmagd et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures





















References
-
- Resistant hypertension - its identification and epidemiology. Sarafidis PA, Georgianos P, Bakris GL. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2013;9:51–58. - PubMed
-
- US trends in prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension, 1988-2008. Egan BM, Zhao Y, Axon RN. JAMA. 2010;303:2043–2050. - PubMed
-
- Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Lancet. 2005;365:217–223. - PubMed
-
- Resistant hypertension: diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Professional Education Committee of the Council for High Blood pressure research. Calhoun DA, Jones D, Textor S, et al. Circulation. 2008;117:0–26. - PubMed
-
- Effectiveness of renal denervation therapy for resistant hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Davis MI, Filion KB, Zhang D, Eisenberg MJ, Afilalo J, Schiffrin EL, Joyal D. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:231–241. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
