Circulating Biomarkers Predict Immunotherapeutic Response in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using a Machine Learning Method
- PMID: 39493265
- PMCID: PMC11531708
- DOI: 10.2147/JHC.S474593
Circulating Biomarkers Predict Immunotherapeutic Response in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using a Machine Learning Method
Abstract
Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy is a promising treatment for cancer. However, the response rate to ICI therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients is low (approximately 30%). Thus, an approach to predict whether a patient will benefit from ICI therapy is required. This study aimed to design a classifier based on circulating indicators to identify patients suitable for ICI therapy.
Methods: This retrospective study included HCC patients who received immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy between March 2017 and September 2023 at Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital and Jinling Hospital. The levels of the 17 serum biomarkers and baseline patients' characters were assessed to discern meaningful circulating indicators related with survival benefits using random forest. A prognostic model was then constructed to predict survival of patients after treatment.
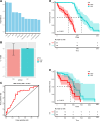
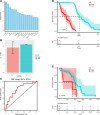
Results: A total of 369 patients (mean age 56, median follow-up duration 373 days,) were enrolled in this study. Among the 17 circulating biomarkers, 11 were carefully selected to construct a classifier. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis yielded an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.724. Notably, patients classified into the low-risk group exhibited a more positive prognosis (P = 0.0079; HR, 0.43; 95% CI 0.21-0.87). To enhance efficacy, we incorporated 11 clinical features. The extended model incorporated 12 circulating indicators and 5 clinical features. The AUC of the refined classifier improved to 0.752. Patients in the low-risk group demonstrated superior overall survival compared with those in the high-risk group (P = 0.026; HR 0.39; 95% CI 0.11-1.37).
Conclusion: Circulating biomarkers are useful in predicting therapeutic outcomes and can help in making clinical decisions regarding the use of ICI therapy.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; immunotherapy; machine learning; predictive model.
© 2024 Dai et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combination of alpha-fetoprotein and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio to predict treatment response and survival outcomes of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors.BMC Cancer. 2023 Jun 15;23(1):547. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11003-0. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37322411 Free PMC article.
-
Prognosis prediction and risk stratification of transarterial chemoembolization or intraarterial chemotherapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma based on machine learning.Eur Radiol. 2024 Aug;34(8):5094-5107. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-10581-2. Epub 2024 Jan 30. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38291256 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic model for predicting outcome and guiding treatment decision for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma treated with lenvatinib monotherapy or lenvatinib plus immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 23;14:1141199. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1141199. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36911686 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive Biomarkers for Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment Response in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 21;24(8):7640. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087640. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single or combined immune checkpoint inhibitors compared to first-line platinum-based chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab for people with advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 30;4(4):CD013257. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013257.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33930176 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cadonilimab, a PD-1/CTLA-4 bispecific antibody in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a real-world study.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2025 Apr 28;74(6):186. doi: 10.1007/s00262-025-04038-8. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2025. PMID: 40293533 Free PMC article.
-
miR-130a-5p/TFPI2 axis promotes invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma by altering epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.Discov Oncol. 2025 Apr 17;16(1):546. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02296-7. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40244374 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

