Isopimpinellin inhibits UVA-induced overproduction of MMPs via suppression of MAPK/AP-1 signaling in human dermal fibroblasts
- PMID: 39493386
- PMCID: PMC11525369
- DOI: 10.1007/s10068-024-01611-2
Isopimpinellin inhibits UVA-induced overproduction of MMPs via suppression of MAPK/AP-1 signaling in human dermal fibroblasts
Abstract
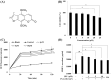
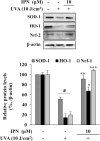
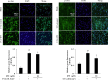
Corydalis heterocarpa is an edible halophyte and an ingredient in traditional Korean medicine. In the present study, isopimpinellin (IPN), a bioactive coumarin, was isolated from the medicinal halophyte C. heterocarpa, and the effects of IPN against UVA-induced photoaging were investigated in human dermal fibroblasts. Photoaging is a skin disorder that manifests itself as premature skin aging due to chronic exposure to UV radiation. The symptoms of photoaging mainly arise from degraded skin connective tissue produced by overly expressed matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). IPN treatment decreased the UVA-induced formation of reactive oxygen species and decreased MMP-1, MMP-3, and MMP-9 collagenases at the protein level. The UVA-mediated suppression of tissue inhibitors of MMP-1 and -2 was attenuated with IPN. The presence of 10 μM IPN inhibited the MAPK-mediated phosphorylation of c-Fos and c-Jun. In conclusion, the overall result of the current study indicated that IPN inhibited the UVA-induced overexpression of MMPs via blocking the MAPK/AP-1 pathway.
Keywords: Corydalis heterocarpa; Human dermal fibroblast; Isopimpinellin; MMP; Photoaging.
© The Korean Society of Food Science and Technology 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
