Single-cell analysis of matrisome-related genes in breast invasive carcinoma: new avenues for molecular subtyping and risk estimation
- PMID: 39493752
- PMCID: PMC11530991
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1466762
Single-cell analysis of matrisome-related genes in breast invasive carcinoma: new avenues for molecular subtyping and risk estimation
Abstract
Background: The incidence of breast cancer remains high and severely affects human health. However, given the heterogeneity of tumor cells, identifying additional characteristics of breast cancer cells is essential for accurate treatment.
Purpose: This study aimed to analyze the relevant characteristics of matrix genes in breast cancer through the multigroup data of a breast cancer multi-database.
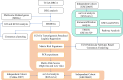
Methods: The related characteristics of matrix genes in breast cancer were analyzed using multigroup data from the breast cancer multi database in the Cancer Genome Atlas, and the differential genes of breast cancer matrix genes were identified using the elastic net penalty logic regression method. The risk characteristics of matrix genes in breast cancer were determined, and matrix gene expression in different breast cancer cells was evaluated using real-time fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR). A consensus clustering algorithm was used to identify the biological characteristics of the population based on the matrix molecular subtypes in breast cancer, followed by gene mutation, immune correlation, pathway, and ligand-receptor analyses.
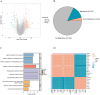
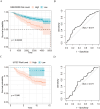
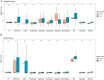
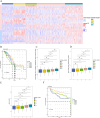
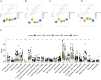
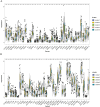
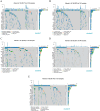
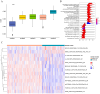
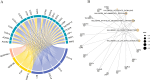
Results: This study reveals the genetic characteristics of cell matrix related to breast cancer. It is found that 18.1% of stromal genes are related to the prognosis of breast cancer, and these genes are mostly concentrated in the biological processes related to metabolism and cytokines in protein. Five different matrix-related molecular subtypes were identified by using the algorithm, and it was found that the five molecular subtypes were obviously different in prognosis, immune infiltration, gene mutation and drug-making gene analysis.
Conclusions: This study involved analyzing the characteristics of cell-matrix genes in breast cancer, guiding the precise prevention and treatment of the disease.
Keywords: breast cancer; cellular matrix gene; matrix score; molecular subtyping; single-cell sequencing.
Copyright © 2024 Su, Wang, Cai, Wang, Wang, Yang, Gong, Fang and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Slamon DJ, Fasching PA, Hurvitz S, Chia S, Crown J, Martín M, et al. . Rationale and trial design of NATALEE: a Phase III trial of adjuvant ribociclib + endocrine therapyversus endocrine therapy alone in patients with HR+/HER2– early breast cancer. Ther Adv Med Oncol. (2023) 15:1–16. doi: 10.1177/17588359231178125 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bidard FC, Kaklamani VG, Neven P, Streich G, Montero AJ, Forget F, et al. . Elacestrant (oral selective estrogen receptor degrader) Versus Standard Endocrine Therapy for Estrogen Receptor-Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Negative Advanced Breast Cancer: Results From the Randomized Phase III EMERALD Trial. J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40:3246–56. doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.00338 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lu Y, Im S, Colleoni M, Franke F, Bardia A, Cardoso F, et al. . Updated Overall Survival of Ribociclib plus Endocrine Therapy versus Endocrine Therapy Alone in Pre- and Perimenopausal Patients with HR+/HER2– Advanced Breast Cancer in MONALEESA-7: A Phase III Randomized Clinical Trial. Clin Cancer Res. (2022) 28:851–59. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-3032 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

