Granulomatous Colitis Due to Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome
- PMID: 39493955
- PMCID: PMC11527421
- DOI: 10.14309/crj.0000000000001477
Granulomatous Colitis Due to Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome
Abstract
Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome (HPS) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by oculocutaneous albinism, bleeding diathesis, and multiorgan involvement. Granulomatous enterocolitis may occur in a subset of patients. Distinguishing HPS from other diseases such as Crohn's disease can be challenging, and managing HPS-associated colitis is complex. Recent reports suggest potential efficacy of infliximab in treating HPS-related granulomatous colitis. Here, we document the case of a 27-year-old patient with genetically confirmed HPS type 1, presenting with granulomatous colitis and successfully treated with corticosteroids and infliximab.
Keywords: Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome; colitis; granulomatous.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American College of Gastroenterology.
Figures

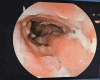
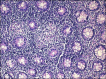

References
-
- Grucela AL, Patel P, Goldstein E, Palmon R, Sachar DB, Steinhagen RM. Granulomatous enterocolitis associated with Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101(9):2090–5. - PubMed
-
- Felipez LM, Gokhale R, Guandalini S. Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome: Severe colitis and good response to infliximab. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2010;51(5):665–7. - PubMed
-
- Hazzan D, Seward S, Stock H, et al. Crohn's like colitis, enterocolitis and perianal disease in Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome. Colorectal Dis. 2006;8(7):539–43. - PubMed
-
- Witkop CJ, Nuñez Babcock M, Rao GH, et al. Albinism and HermanskyPudlak syndrome in Puerto Rico. Bol Asoc Med P R. 1990;82(8):333–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

