Long Lasting Insecticide-Treated Nets Utilization and Associated Factors Among Pregnant Women in Shebel Berenta District, Northwest Ethiopia
- PMID: 39494047
- PMCID: PMC11528622
- DOI: 10.1177/11786302241291957
Long Lasting Insecticide-Treated Nets Utilization and Associated Factors Among Pregnant Women in Shebel Berenta District, Northwest Ethiopia
Abstract
Background: Insecticide-treated bed nets are cost-effective vector control methods for malaria prevention. Malaria during pregnancy poses a significant health problem in Ethiopia. This study aimed to assess insecticide-treated nets utilization and associated factors among pregnant women in Shebel Berenta District, Northwest Ethiopia.
Objective: To assess insecticide-treated bed nets utilization and associated factors among pregnant women in Shebel Berenta District, Northwest Ethiopia, in 2023.
Methods: A community-based cross-sectional study was conducted from March 15 to April 30, 2023, on 505 randomly selected pregnant women. Data were collected using a pre-tested structured questionnaire and observational checklist, analyzed with EpiData 3.1 and SPSS 25. Significant factors associated with long-lasting insecticide-treated nets were identified (P < .05, 95% CI) and were reported as statistically significant factors associated with the utilization of insecticide-treated bed nets.
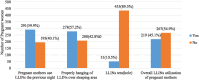
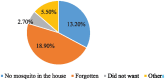
Results: The utilization of long-lasting insecticide-treated nets was 45.10% [95% CI: 40.5%-49.2%]. Mothers who had antenatal care follow-up (AOR = 3.359; 95%CI: 1.829, 6.166), mothers with illiterate educational status (AOR = 0.196; 95%CI: 0.064-0.603), and mothers who had received information (message) (AOR = 8.102; 95%CI: 3.942-16.653) were significantly associated with long lasting insecticide-treated net utilization.
Conclusion: Utilization of long lasting insecticide-treated nets by pregnant women was 45.1%, which was lower than the WHO standard. Attending antenatal care, receiving information (messages) about malaria and long lasting insecticide-treated net, and mother's being literate had a substantial impact on long lasting insecticide-treated net utilization. Therefore, efforts should be made to strengthen ANC service, health information and women's educational status to increase utilization of long lasting insecticide-treated nets.
Keywords: Ethiopia; Pregnant women; long lasting insecticide-treated nets; utilization.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Operational Manual on Leishmaniasis Vector Control, Surveillance, Monitoring and Evaluation. World Health Organization; 2022.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous