Research progress of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) in prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease
- PMID: 39494241
- PMCID: PMC11527678
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1477636
Research progress of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) in prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease
Abstract
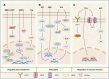
Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) contains a variety of biologically active compounds, including flavonoids, terpenoids, polysaccharides, organic acids, volatile oils, and vitamins. It has been demonstrated to be effective in the treatment of cardiovascular disorders. In this paper, we evaluated the pharmacological effects of sea buckthorn in cardiovascular diseases through preclinical studies, and revealed the mechanism of action of the active components in sea buckthorn in cardiovascular diseases, including anti-inflammatory, lipid oxidation regulation, antioxidant, vascular function modulation, anti-platelet aggregation, autophagy, intestinal microorganism regulation, and cell apoptosis reduction. In clinical trials, sea buckthorn was proven to be effective in managing lipid metabolism, blood pressure, and blood glucose levels in patients. We also extensively reviewed the safety of sea buckthorn medicine and its toxicity to numerous organs. To summarize, sea buckthorn has a beneficial effect on cardiovascular disease and may give a novel strategy for clinical intervention and therapy. This paper summarizes the phytochemistry, pharmacology, clinical applications, safety, and toxicity of sea buckthorn in order to better understand the mechanism of action of the various bioactive components in sea buckthorn, investigate its medicinal potential, and provide more options for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; clinical application; pharmacology; phytochemistry; sea buckthorn.
© 2024 Chen, He, Cao, Wang, Liu, Wang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Zoccali C, Mallamaci F, Adamczak M, de Oliveira RB, Massy ZA, Sarafidis P, et al. Cardiovascular complications in chronic kidney disease: a review from the European renal and cardiovascular medicine working group of the European Renal Association. Cardiovasc Res. (2023) 119(11):2017–32. 10.1093/cvr/cvad083 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

