NLC Delivery of EGFP Plasmid to TM4 Cell Nuclei for Targeted Gene Therapy
- PMID: 39494265
- PMCID: PMC11530889
- DOI: 10.34172/apb.2024.050
NLC Delivery of EGFP Plasmid to TM4 Cell Nuclei for Targeted Gene Therapy
Abstract
Purpose: This study evaluated whether a nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC) delivery system could safely and accurately deliver nucleic acids to the cell nucleus using the enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP)-C1 plasmid model.
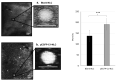
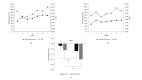
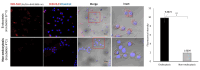
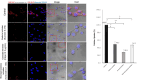
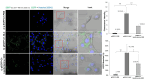
Methods: The NLC was formulated using the emulsification method and equipped for cationic lipid-mediated transfection with 1,2-dioleoyl-3-trimethylammonium-propane (DOTAP), which interacts electrostatically with nucleic acid. The NLC attributes, including size, polydispersity index, and zeta potential, were assessed by dynamic light scattering (DLS). The morphological structure was analyzed using transmission electron microscopy. Entrapment efficiency was evaluated by a direct method. Cellular uptake mechanisms of pEGFP-C1-NLC and the ability of pEGFP-C1 to penetrate the nucleus of TM4 cells to express EGFP were observed using confocal microscopy.
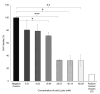
Results: pEGFP-C1-NLC exhibited particle sizes in the range 56-88 nm with a particle charge range of -6.0 to+1.3 mV. The polydispersity index<0.5 showed good size uniformity, and entrapment efficiency of pEGFP-C1in the NLC was 92.06±2.295%. The NLC formulation was internalized predominantly via caveolae-mediated endocytosis, as indicated by EGFP expression following successful delivery of pEGFP by the NLC into the cells.
Conclusion: NLC formulation could deliver genetic material to the nucleus and could be considered a gene therapy candidate for spermatogenesis.
Keywords: Cellular uptake; Delivery system; EGFP; NLC; Nucleic acid; Nucleus.
©2024 The Author (s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nanostructured lipid carriers as novel drug delivery system for lung cancer gene therapy.Pharm Dev Technol. 2016;21(3):277-81. doi: 10.3109/10837450.2014.996900. Epub 2015 Jan 5. Pharm Dev Technol. 2016. PMID: 25560648
-
Transferrin-modified nanostructured lipid carriers as multifunctional nanomedicine for codelivery of DNA and doxorubicin.Int J Nanomedicine. 2014 Aug 25;9:4107-16. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S67770. eCollection 2014. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014. PMID: 25187713 Free PMC article.
-
Formulation and in vitro characterization of domperidone loaded solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers.Daru. 2011;19(1):23-32. Daru. 2011. PMID: 22615636 Free PMC article.
-
Quality by design (QbD) optimization of diazepam-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) for nose-to-brain delivery: Toxicological effect of surface charge on human neuronal cells.Int J Pharm. 2021 Sep 25;607:120933. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.120933. Epub 2021 Jul 27. Int J Pharm. 2021. PMID: 34324988
-
Formulation and evaluation of lidocaine lipid nanosystems for dermal delivery.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2009;10(3):985-92. doi: 10.1208/s12249-009-9287-1. Epub 2009 Jul 30. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2009. PMID: 19641997 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kojima Y, Mizuno K, Umemoto Y, Sasaki S, Hayashi Y, Kohri K. Therapeutic potential of gene transfer to testis; myth or reality? In: Kang C, ed. Gene Therapy Applications. IntechOpen; 2011. p. 492. 10.5772/20488. - DOI
-
- Shi F, Zhang Z, Cui H, Wang J, Wang Y, Tang Y, et al. Analysis by transcriptomics and metabolomics for the proliferation inhibition and dysfunction through redox imbalance-mediated DNA damage response and ferroptosis in male reproduction of mice and TM4 Sertoli cells exposed to PM25. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022;238:113569. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113569. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous